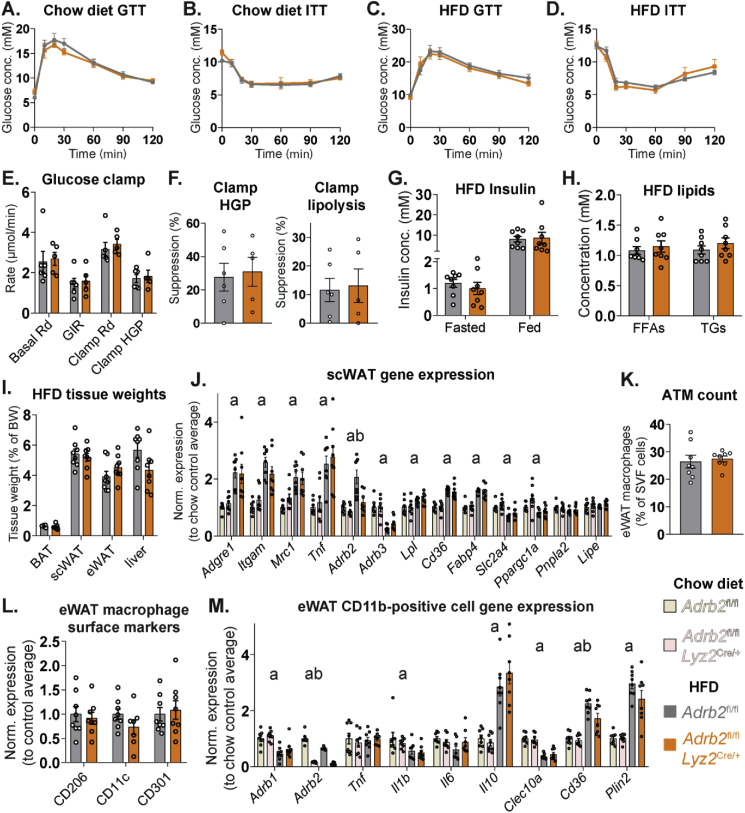
Figure 5.
Unaltered development of WAT inflammation and systemic insulin resistance in HFD-fed macrophage-specific Adrb2 knockout mice. Glucose excursion curves during intraperitoneal (A) glucose and (B) insulin tolerance tests in Adrb2fl/fl (n = 8) and Adrb2fl/flLyz2Cre/+ (n = 8) chow-fed 5-month-old male mice. Glucose excursion curves during intraperitoneal (C) glucose and (D) insulin tolerance tests in Adrb2fl/fl (n = 8) and Adrb2fl/flLyz2Cre/+ (n = 8) 5-month-old male mice, fed HFD for 10–11 weeks. (E) Glucose disposal rates (Rd) in basal and hyperinsulinemic (Clamp) states, glucose infusion rates and hepatic glucose production rate during hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic glucose clamp experiment in Adrb2fl/fl (n = 6) and Adrb2fl/flLyz2Cre/+ (n = 5) 5-month-old male mice, fed HFD for 12 weeks. (F) Suppression of hepatic glucose production rate and lipolysis rate in the hyperinsulinemic state of glucose clamp experiment. (G) Serum insulin measured after 16-hour fast or in a random fed state, and (H) serum free fatty acid and triglyceride levels, measured in a random fed state in Adrb2fl/fl (n = 8) and Adrb2fl/flLyz2Cre/+ (n = 8) 5-month-old male mice, fed HFD for 12 weeks. (I) Indicated tissue weights, (J) qPCR analysis of indicated gene expression in scWAT, (K) flow cytometry quantification of eWAT macrophage number and (L) the expression of indicated surface proteins in the macrophage population (normalized to the average of Adrb2fl/fl group) (M) qPCR expression analysis of indicated genes in the CD11b-positive eWAT cell fraction from Adrb2fl/fl (n = 8) and Adrb2fl/flLyz2Cre/+ (n = 8) 5-month-old male mice, fed HFD for 12 weeks. In (J, M), samples were analyzed together with corresponding Adrb2fl/fl (n = 8) and Adrb2fl/flLyz2Cre/+ (n = 8) age-matched male chow-fed control samples, and data was normalized to Adrb2fl/fl chow-fed control group average. All graphs show means ± SEM. In (J, M), a indicates p < 0.05 for diet effect factor and b indicates p < 0.05 for genotype effect factor in a two-way ANOVA.