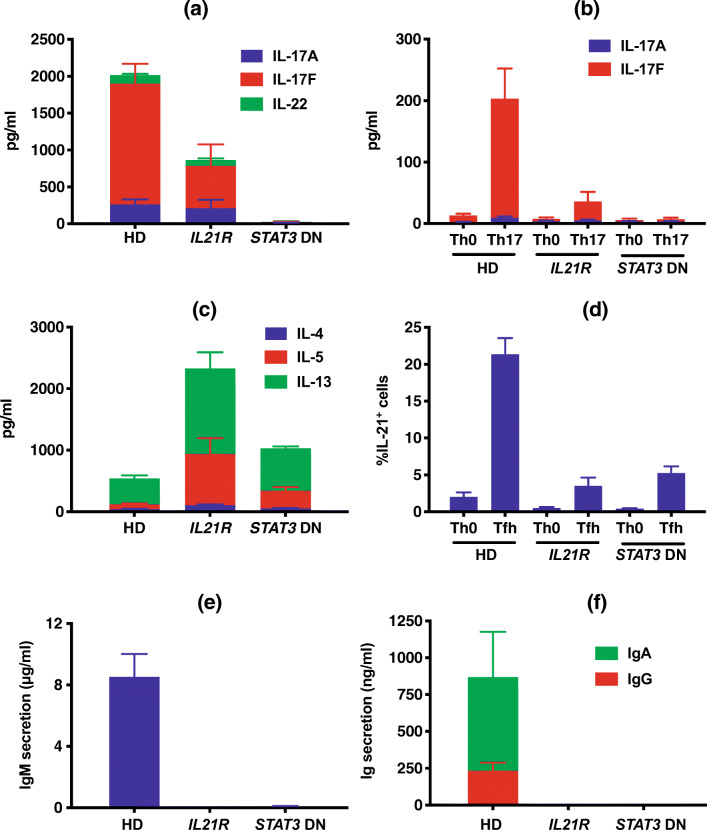
Fig. 7.
Functional defects in B and T cells due to inactivating biallelic IL21R variants. a–d Memory (a, c) or naïve (b, d) CD4+ T cells were sort-purified from healthy donors (HD, n = 22–24), or individuals with biallelic variants in IL21R (IL21R, n = 6) or DN variants in STAT3 (STAT3 DN, n = 6–9), and then cultured for 5 days in vitro under non-polarizing Th0 conditions (a, c), Th17 conditions (b) or Tfh-polarizing conditions (d). Secretion of the indicated Th17 (a, b; IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-22) or Th2 (c; IL-4, IL-5, IL-13) cytokines, or expression of the Tfh-cytokine IL-21 (d) was then determined. e, f Naive B cells were sort-purified from healthy donors (HD, n = 35), or individuals with biallelic variants in IL21R (IL21R, n = 6) or STAT3 DN variants (n = 10), and then cultured for 7 days in vitro with CD40L and IL-21. Secretion of IgM (e) or IgG and IgA (f) was then determined. NB: the data depicted in these graphs has been presented in previous publications [26, 33, 34], but is reproduced here to enable comparison between flow cytometric and functional defects, as well as clinical features, resulting from IL-21R deficiency and STAT3 DN mutations