Table 2.
Different types and main characteristics of controlled drug delivery systems for biomedical applications [141, 142]
| Controlled drug delivery system | Material | Size | Structure | Types | Fabrication methods | Morphology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liposomes |
Cholesterol Phospholipids |
20 nm–10 µm | Lipid based spherical shaped vesicular systems |
Multilamellar Single compartment Macrovesicles |
Solvent evaporation Solvent dispersion Reverse phase evaporation |

|
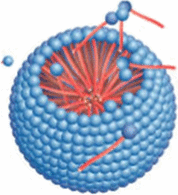
| Micelles | Phosphatidyl ethanolamine, Phosphatidyl choline, PEG, PVP, PEOz, PEO, PCL, PLA… | 10–200 nm | Hydrophilic inner core–Hydrophobic shell architecture |
Polymeric micelles Lipid micelles Supermicelles |
Solvent evaporation Direct dilution Salting out Dialysis Flash nanoprecipitation |
|
| Nanoparticles | PLGA, PEG, PCL, Chitosan, Cholesterol, Palmitate, Au, Si, Ag, Fe, Cu, Pb… | 10–300 nm | Nanocapsules, nanospheres, porus speheres |
Polymeric Lipid Metal Gold/Silver Magnetic Silica |
Solvent evaporation Double emulsion Homogenization Salting out NaBH4 reduction Sol–Gel synthesis |

|
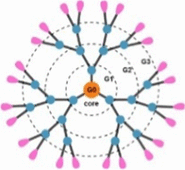
| Dendrimers | PAMAM, PPI | 20–400 nm | Macromolecules with a regularly branched tree-like structure | Simple, Chiral, Micellar, Hybrid, Metallo dendrimers |
Divergent synthesis Convergent synthesis Self-assembly synthesis |
|
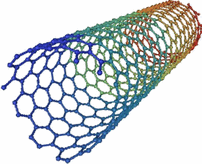
| Carbon nanotubes | Carbon atoms | 0.5–50 nm Ø | Rolled sheets of graphene rings built from sp2 hybridized carbon atoms | SWCNTs, MWCNTs |
Laser vaporization Chemical vapor deposition Arc discharge |
|
| Hydrogels | Fibrin, collagen, hyaluronic acid, PEG, PVA, PAAM… | – | Natural/ synthetic cross-linked polymers containing a large amount of water |
Temperature-responsive hydrogels, pH-responsive hydrogels, Electric-sensitive hydrogels, Ionic strength-sensitive hydrogels |
Three-dimensional printing Layer-by-Layer fabrication Microfluidic-based fabrication |
|
| Quantum dots | CdSe, CdS, ZnS, PbS… | 5–50 nm | Nanosized semiconductor particles with optical and electronic properties | Imaging QDs, Drug delivery QDs, Sensor applications QDs |
Colloidal synthesis Plasma synthesis Self-assembled synthesis High temperature dual injection |
|
| Polyelectrolyte complexes | Chitosan, PGA, SDS, CMCG, fibroin, SCMC… | 20–300 nm |
Polymeric matrix with oppositely charged polyelectrolytes with strong but reversible electrostatic links |
Nonstoichiometric water-soluble PECs, Stoichiometric insoluble PECs, Turbid colloidal stable PECs, Complex coacervates PECs |
Solution spontaneous association Simple PECs titration technique |

|
CMCG, carboxymethyl cashew gum; MWCNTs, Multiple-walled carbon nanotubes; PAAM, poly(acrylamide); PAMAM, poly (amido amine); PCL, Poly (ε-caprolactone); PEG, Poly (ethylene glycol); PEO, poly (propylene oxide); PEOz, poly (2-ethyl-2-oxazoline); PGA, polygalacturonic acid; PLA, poly (lactide); PLGA, poly (lactic-co-glycolic); PPI, poly(propylenemine); PVP, poly (N-vinyl pyrrolidone); SCMC, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose; SDS, sodium dextran sulfate; SWCNTs, Single-walled carbon nanotubes
