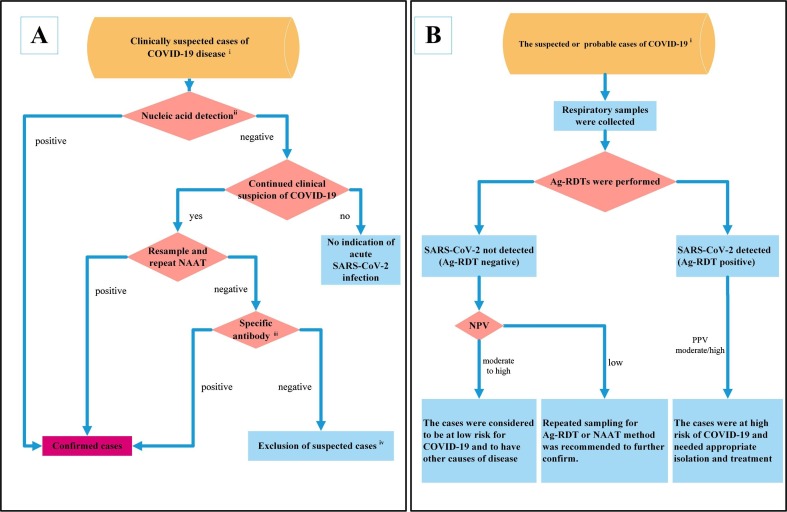
Fig. 1.
Laboratory diagnosis flowchart of COVID-19. A: Diagnostic roles of nucleic acids and antibodies in COVID-19. i: Clinically suspected cases need to meet the epidemiological history and clinical manifestations of COVID-19. ii: Nucleic acid detection generally includes two methods: gene sequencing and NAAT. Any one of them can be used for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. iii: Specific antibody (IgM and IgG) detection is recommended in both the acute phase and convalescent phase to observe seroconversion or an increase in antibody titer. iv: Exclusion of suspected cases needs to meet criteria for SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid and antibody negativity. B: Potential diagnostic roles of Ag-RDTs in COVID-19. With high expected prevalence, the WHO recommends Ag-RDTs to identify SARS-CoV-2 infection in the early stage when NAAT is unavailable or not sufficient. i: A case needs to meet the definition of suspected or probable COVID-19 provided by the WHO. NPV: negative predictive value; PPV: positive predictive value.