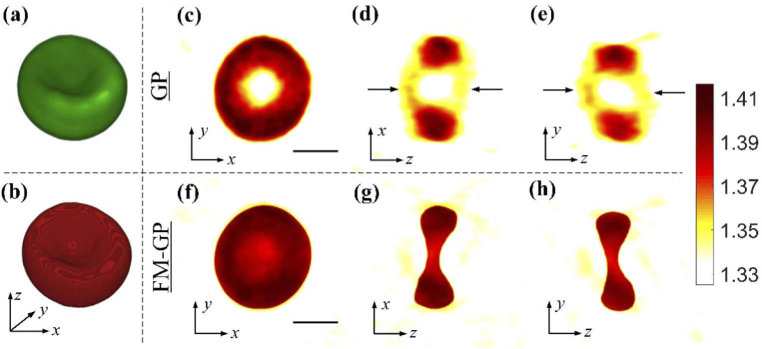
Fig. 5.
Comparison of the reconstructed 3D RI maps of a red blood cell between our method and the conventional ODT method. (a) 3D fluorescence image obtained by SDCM. (b) The corresponding 3D calculated mask. (c-e) Cross sectional slices of the reconstructed RI obtained from the conventional ODT algorithm with 9 projections. (c) x-y slice, (d) x-z slice, and (e) y-z slice, at the center. There are strong deformations breaking the true concave shape of the RBC in (d) and (e), as indicated by black arrows, which are results of missing cone problem in the conventional method. (f-h) The corresponding improved cross sectional slices of the reconstructed RI obtained from our method. This reconstruction coincides well with the true shape of the cell. Scale bars indicate 3 μm.