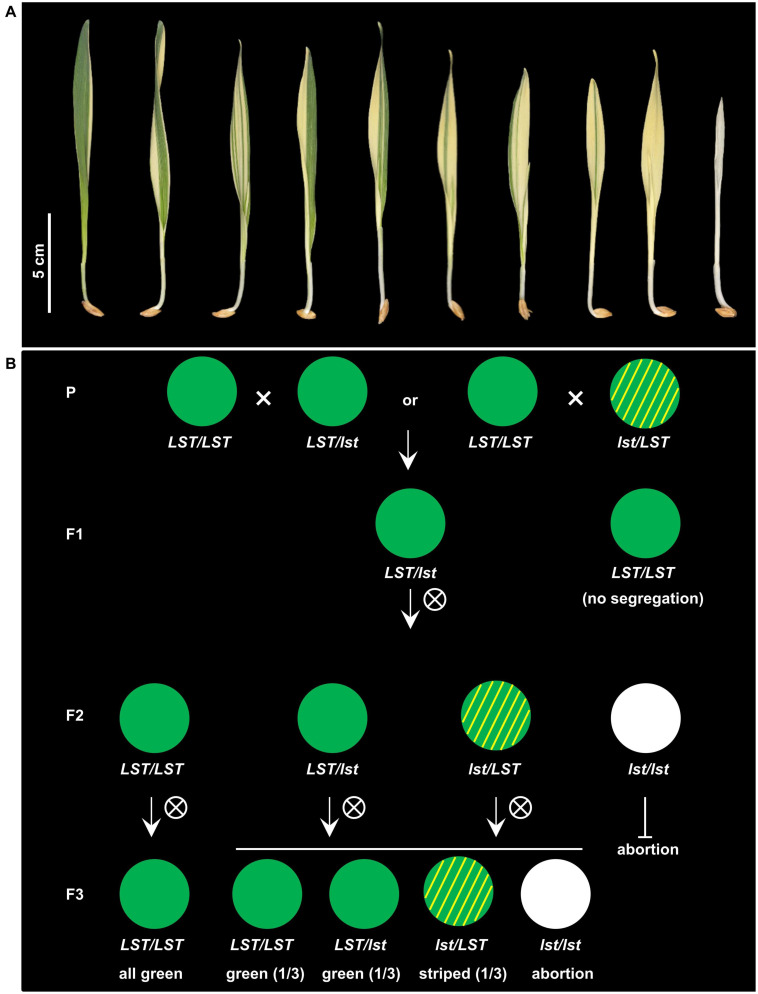
FIGURE 1.
Phenotype and inheritance of variegation in the barley mutant luteostrians. (A) Penetration of the mutant phenotype varies among seedlings, ranging from a narrow yellow stripe to complete yellowish or albino. Neither yellowish/albino plants survived beyond third-leaf stage. (B) Inheritance pattern of the luteostrians mutant phenotype. Variegation only occurs in plants if the lst allele was transmitted through the female gamete. Upper panel: Heterozygous plants can be obtained by using either green or variegated plants (heterozygous for the luteostrians allele) as pollen donor. This will generate 50% F1-progeny heterozygous for luteostrians (panel F1). Progenies of selfed F1 heterozygotes will exhibit Mendelian segregation in F2; the variegated phenotype, however, will appear only in 50% of the heterozygous plants, carrying the mutant allele inherited from F1 female gamete. Zygotes homozygous for the luteostrians allele will be aborted as homozygosity of luteostrians early zygotic lethal. Lower panel: Green phenotype of homozygous wild type plants in F2 will be stably transmitted in F3; progenies of heterozygous F2 plants follow a Mendelian inheritance pattern in F3.