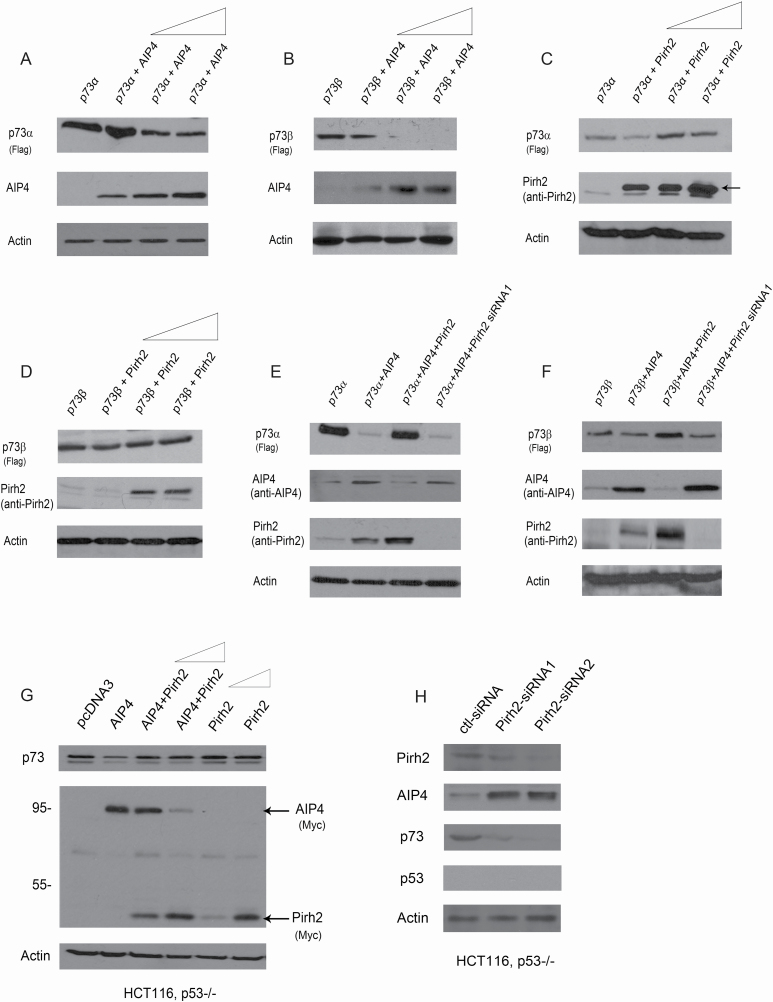
Figure 4.
Pirh2 and AIP4 both regulate p73 expression. (A) H1299 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing p73α, along with increased amounts of Myc-AIP4 (5, 10 and 20 µg). Western blot analysis was performed using a Flag antibody to detect p73α, and a Myc antibody for AIP4. (B) Similar to (A), except that p73β was used. (C) Similar to (A), except that H1299 cells were transfected with p73α, along with increased amounts of the Pirh2 expression construct (5, 10 and 20 µg). (D) Similar to (C), except that p73β was used. (E) H1299 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing p73α, in combination with AIP4, AIP4 and Pirh2, or transfected p73α and AIP4 in Pirh2-depleted H1299 cells, as indicated. The p73α, AIP4 and Pirh2 protein levels were detected by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (F) Similar to (E), except that p73β was used. (G) HCT116, p53−/− cells were transfected with plasmids expressing AIP4, or with AIP4 and increased amounts of Pirh2 (5 and 10 µg) or with increased amounts of Pirh2 expression plasmid (5 and 10 µg), and analyzed by western blotting with indicated antibodies. The p73, AIP4 and Pirh2 protein levels were detected by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (H) HCT116, p53−/− cells were transfected with control-siRNA, or Pirh2-siRNA1 or Pirh2-siRNA2. The levels of endogenous Pirh2, AIP4, p73 and p53 proteins were detected by western blotting. Actin was used as a loading control.