Figure 5: KRAS4B and MARCKS are regulated by a similar polybasic, PKC-dependent, membrane binding domain.
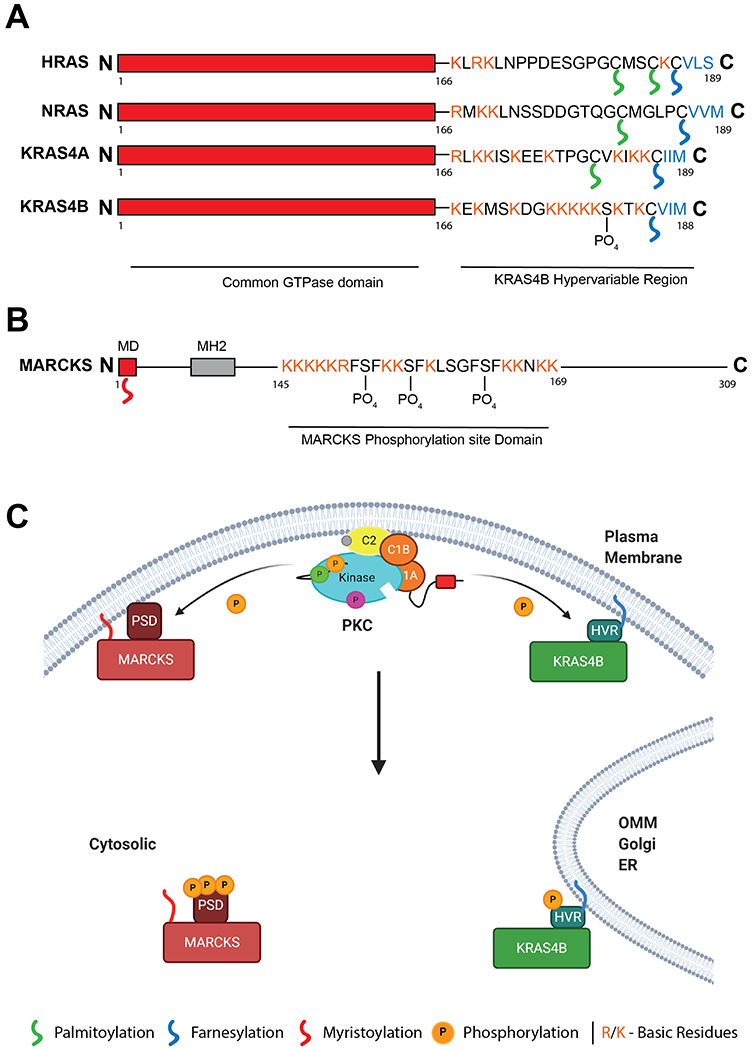
A. Domain structure of HRAS, NRAS and KRAS4A/B, differing in their C-terminal hypervariable region (HVR). KRAS4B HVR contains a single lipid modification however is binds the membrane through a polybasic sequence. This sequence can be phosphorylated by PKC at Ser181. B. Domain structure of PKC substrate MARCKS. N-terminal myristoylation domain (MD) is modified upon translation. A polybasic stretch in the middle of the protein enhances membrane binding and is modified by PKC at 3 sites. C. Model of KRAS4B and MARCKS response to intracellular Ca2+. Activation of PKC by intracellular Ca2+ signals leads to phosphorylation of the MARCKS PSD and the KRAS4B HVR. Upon phosphorylation both proteins translocate from the plasma membrane to intracellular localisations such as the Outer Mitochondrial Membrane (OMM), Golgi, or Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER). Created with BioRender.com
