Figure 1.
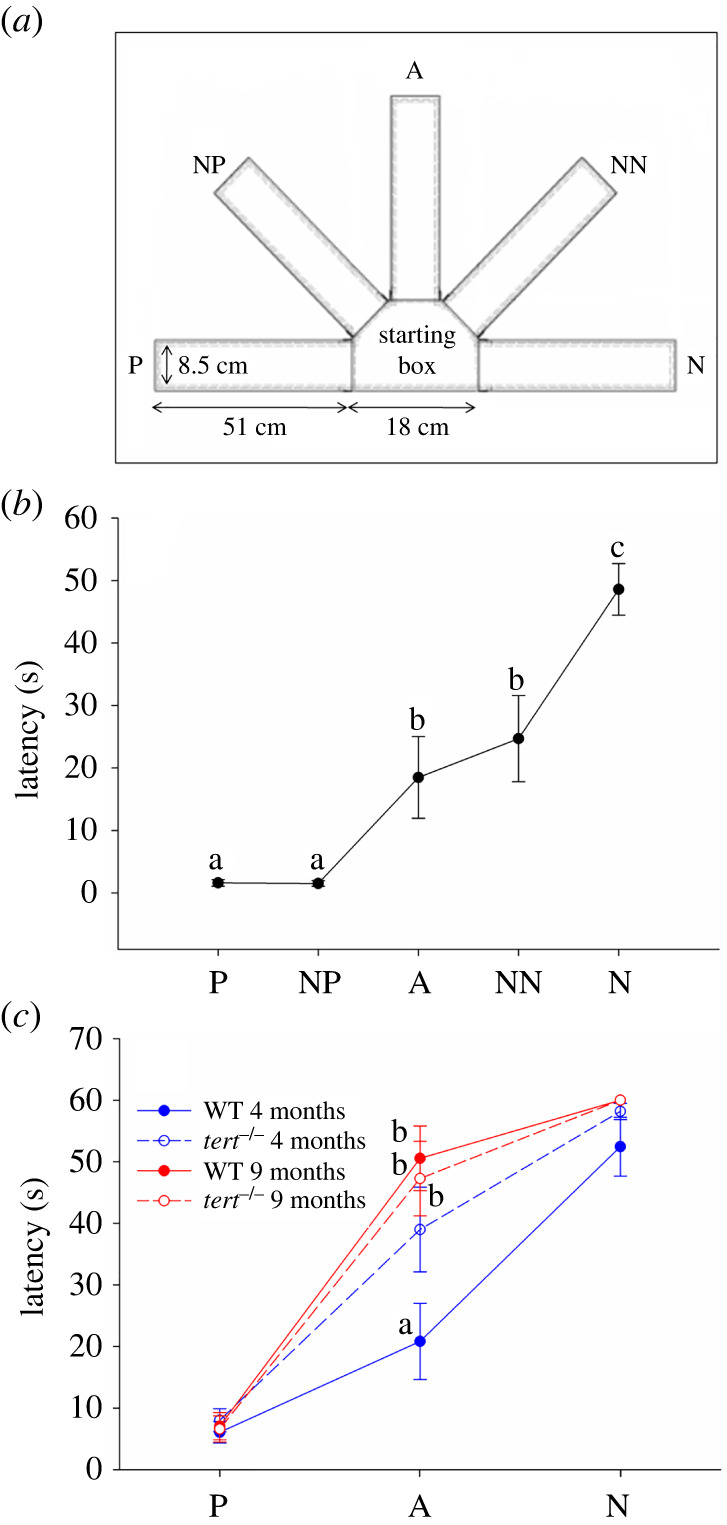
Judgement bias in zebrafish. (a) Diagram of the experimental setup showing the two reference locations (i.e. positive/rewarded (P) and negative/aversive (N)) and the three ambiguous locations (i.e. near-positive (NP), ambiguous (A) and near-negative (NN)). Each location is associated with a specific colour cue. The test consists in training the fish to discriminate between the P and the N location/colour cue. Once fish are able to discriminate between them (as indicated by different latencies in entering into each one), their responses to ambiguous locations/colour cues between the positive and the negative are tested. (b) Mean latencies during the test phase (Experiment 1) on trials performed for the P and N training locations/colour cues, and for the three ambiguous locations/colour cues (NP, A and NN; n = 14 male fish); different letters indicate significant differences between groups following post hoc multiple comparisons tests. (c) Performance of tert−/− mutants and WT siblings (Experiment 2) at different ages (n = 10–12 male fish per Genotype (WT or tert−/−) and Age (four or nine months old)) in the judgement bias paradigm. Different letters indicate significant differences between genotype and age groups for each Treatment (P, A, N) following planned comparisons tests. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m.
