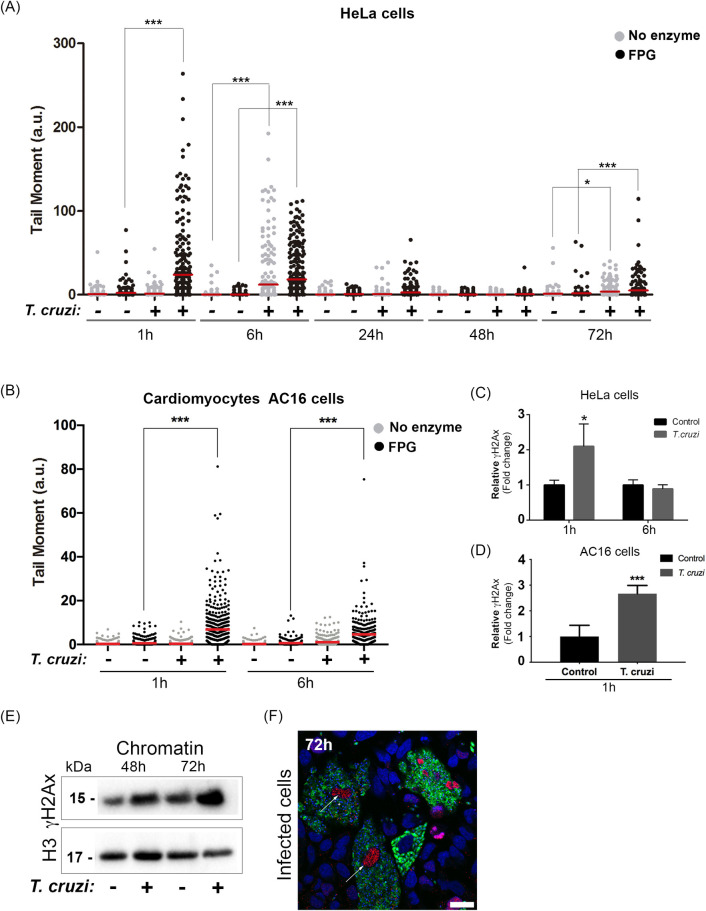
Fig 1. Trypanosoma cruzi induces DNA lesions at early and late stages of infection.
Comet assay was performed in HeLa cells infected (+) or not (-) with trypomastigotes. Cells nuclei were treated with Formamidopyrimidine DNA glycosylase enzyme (FPG; black dots) or not (No enzyme; grey dots). In (A) tail moment quantification (ratio of the tail by the head length) 1 h, 6 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h infected HeLa cells and (B) 1 h and 6 h AC16 cells post-infection. It was performed 3 independent experiments and at least 100 cells were analyzed per experiment; The mean is represented the red line in the graph. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001. H2Ax phosphorylated (γH2Ax) was assessed by flow cytometry after (C) 1 h and 6 h of infected HeLa cells and (D) 1 h infected AC16 cells. The graph represents a relative increase in mean fluorescence from infected cells (T. cruzi) compared to uninfected cells (control). Three independent experiments in duplicate were performed. Bars represent the mean and standard deviation. (E) Isolated chromatin from infected cells (+) or not (-) (48 h and 72 h) were immunoblotted with anti-γH2Ax. Anti-histone 3 (H3) was used as a loading control. (F) Infected cells with T. cruzi-GFP (green) after 72 h were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and stained with mAb yH2Ax (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI probe (blue). Scale bar 10 μm.