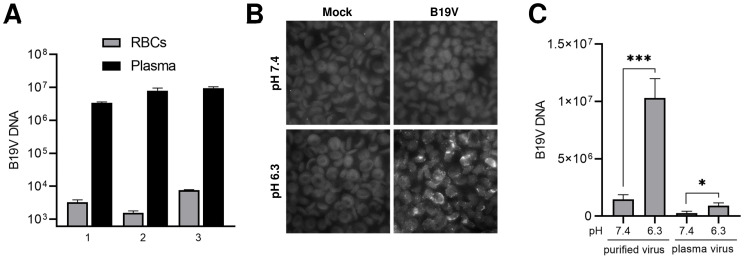
Fig 8. Erythrocytes do not play a significant role as viral decoy targets during B19V viremia.
(A) Freshly collected blood samples (with EDTA as anticoagulant) and tested negative for antibodies against B19V, were spiked with B19V (109 virions) and incubated for 1h at 37°C. The plasma and the RBC fractions were separated by centrifugation, the RBCs were washed with PBS (pH 7.4) and the viral DNA was extracted from both fractions and quantified by qPCR. (B) Detection of B19V in the RBC fraction by IF with an antibody against intact capsids (860-55D). (C) A component(s) in human plasma inhibits binding of B19V to RBCs. RBCs (0.5% in 100 μl PiBS) were incubated at pH 7.4 or 6.3 with B19V (5x109) directly from an infected plasma sample or after purification by iodixanol density gradient centrifugation. After 1h at room temperature, the erythrocytes were washed four times with the corresponding buffer and viral DNA was extracted and quantified. The results are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001.