Extended Data Fig. 7. Expression of FASTKD5 in Jurkat cells and primary human CD4 T cells.
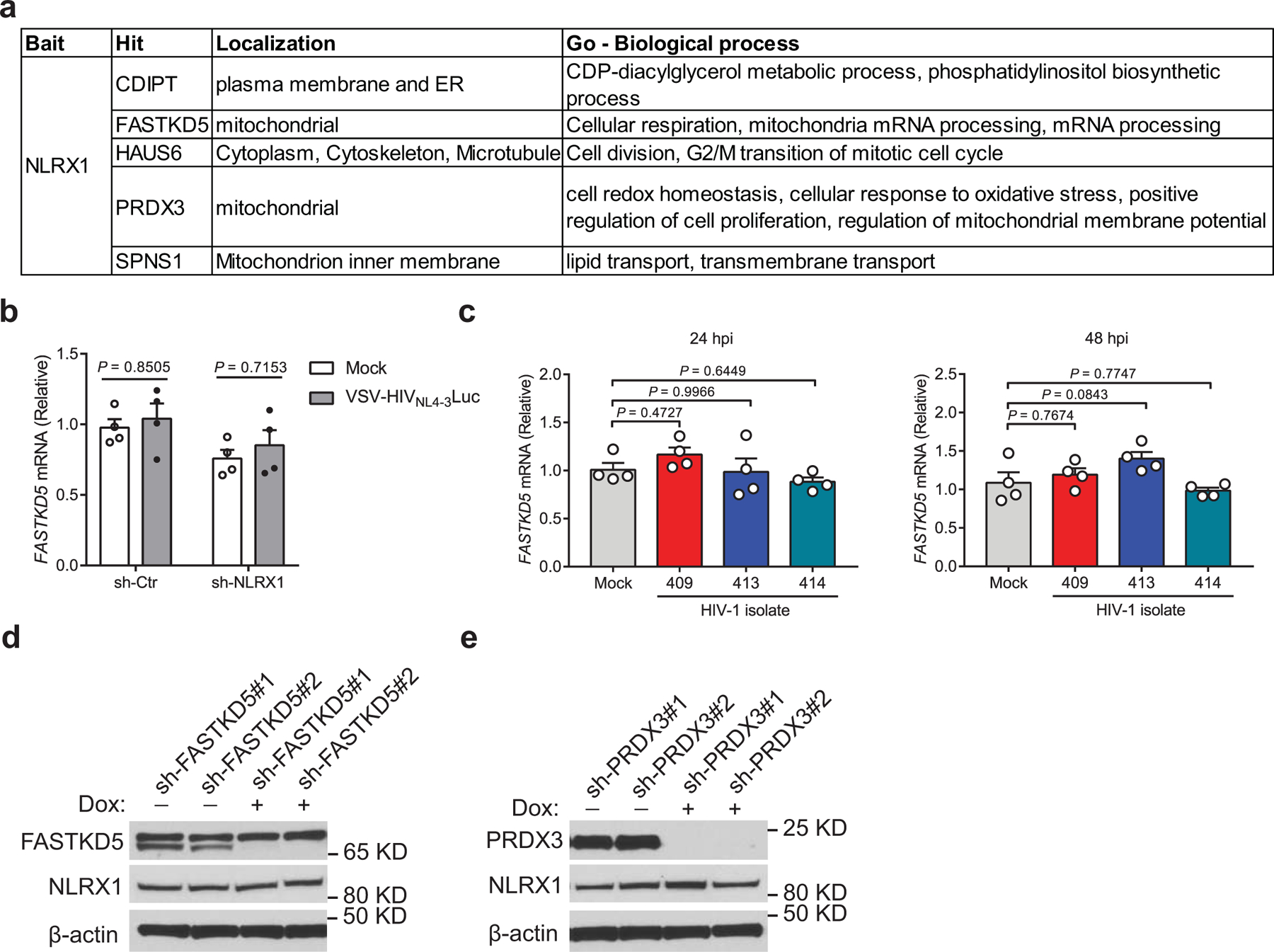
a. Candidates of NLRX1 interacting proteins identified by immunoprecipitation (IP)-mass spectrometry (MS) using overexpressed NLRX1 as the bait in a previous publication.
b. Jurkat-sh-Ctr and Jurkat-sh-NLRX1 cells were left uninfected (mock) or infected by VSV-G-NL4–3-Luc pseudovirus (MOI = 1). FASTKD5 transcripts were assessed at 24 hpi by qPCR. Data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m. n = 4 cell cultures per experiment. Statistical significance was tested by two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test.
c. CD3/CD28 antibody-activated human primary CD4 T cells were infected by three different HIV-1 clinical isolates (10 ng p24), and FASTKD5 transcripts were assessed at 24 and 48 hpi by qPCR. Data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m. n = 4 cell cultures per experiment. Statistical significance was tested by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.
d, e. Doxycycline-induced silencing of FASTKD5 (d) and PRDX3 (e) in Jurkat cells transduced by 2 different shRNA containing lentiviruses. β-actin was used as the loading control.
Data (b – e) are representative of three independent experiments.
