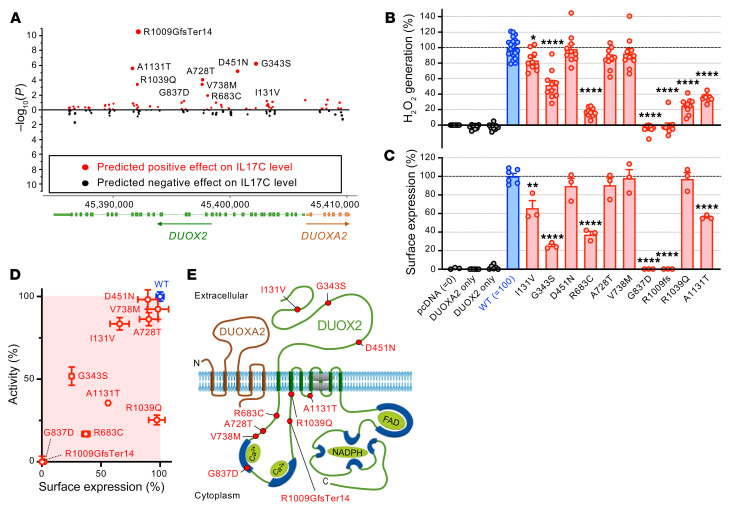
Figure 3. Rare DUOX2 protein variants linked to excessive plasma IL-17C levels impair the expression of a functional DUOX2/DUOXA2 enzyme complex.
(A) Identification of variants significantly contributing to the association with plasma concentration of IL-17C in the study cohort (Wald χ2 test). (B) Extracellular H2O2 production of DUOX2 protein variants expressed in a heterologous system (9). pcDNA: transfections with empty vector; DUOXA2 only: transfections with DUOXA2 only; DUOX2 only: transfections with DUOX2 only; all other transfections are cotransfections of the indicated DUOX2 plasmids (WT or variant) with DUOXA2. Data were obtained from 3 independent transfection experiments each with 3–4 (WT: 6–8) replicates and are mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. (C) Quantitation of DUOX2 cell-surface expression by flow cytometry (see Supplemental Figure 2 for details). Data represent means ± SEM from 3 independent transfection experiments, each including all variants and duplicate transfections of the reference DUOX2 plasmid. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. (D) Summary of the functional assessment of rare DUOX2 protein variants. Data are mean ± SEM. (E) DUOX2 topology model depicting the location of tested variants. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001.