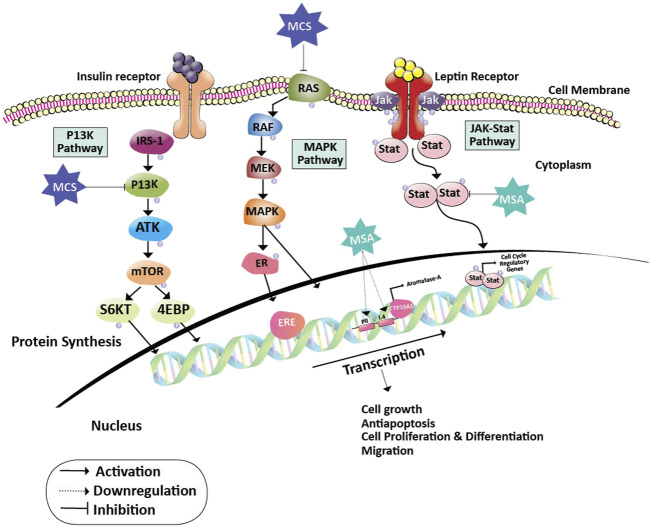
FIGURE 2.
Action of Methylseleninic acid and Selenocysteine on oncogenic pathways. Inhibition of PI3K and RAS proteins by MCS halts the activation of transcription factors (S6KT and 4EBP) and MAPK pathway which is essential for the activation of cell cycle regulatory genes. Whereas, MSA down-regulates the PII and I.4 promoters of the aromatase gene leading to the formation of inadequate levels of estrogen. The action of MCS and MSA on their respective targets helps in the prevention of cancer cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, migration, and induces apoptosis. Abbreviations: 4EBP, Eukaryotic Translation initiation factor 4E binding protein; CYP19A2, Cytochrome P450 Aromatase; ER, Estrogen receptor protein; ERE, Estrogen responsive element; IRS-1, Insulin receptor substrate; JAK, Janus kinase; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCS, Methylselenocysteine; MEK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTOR, Mammalian target of rapamycin; MSA, Methylseleninic acid; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RAF, Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma; RAS, Rat sarcoma; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; S6KT, Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1; Stat, signal transducer and activator of transcription.