Extended Data Fig. 8. Generation, genotyping, and characterization of Tie1-2A mice.
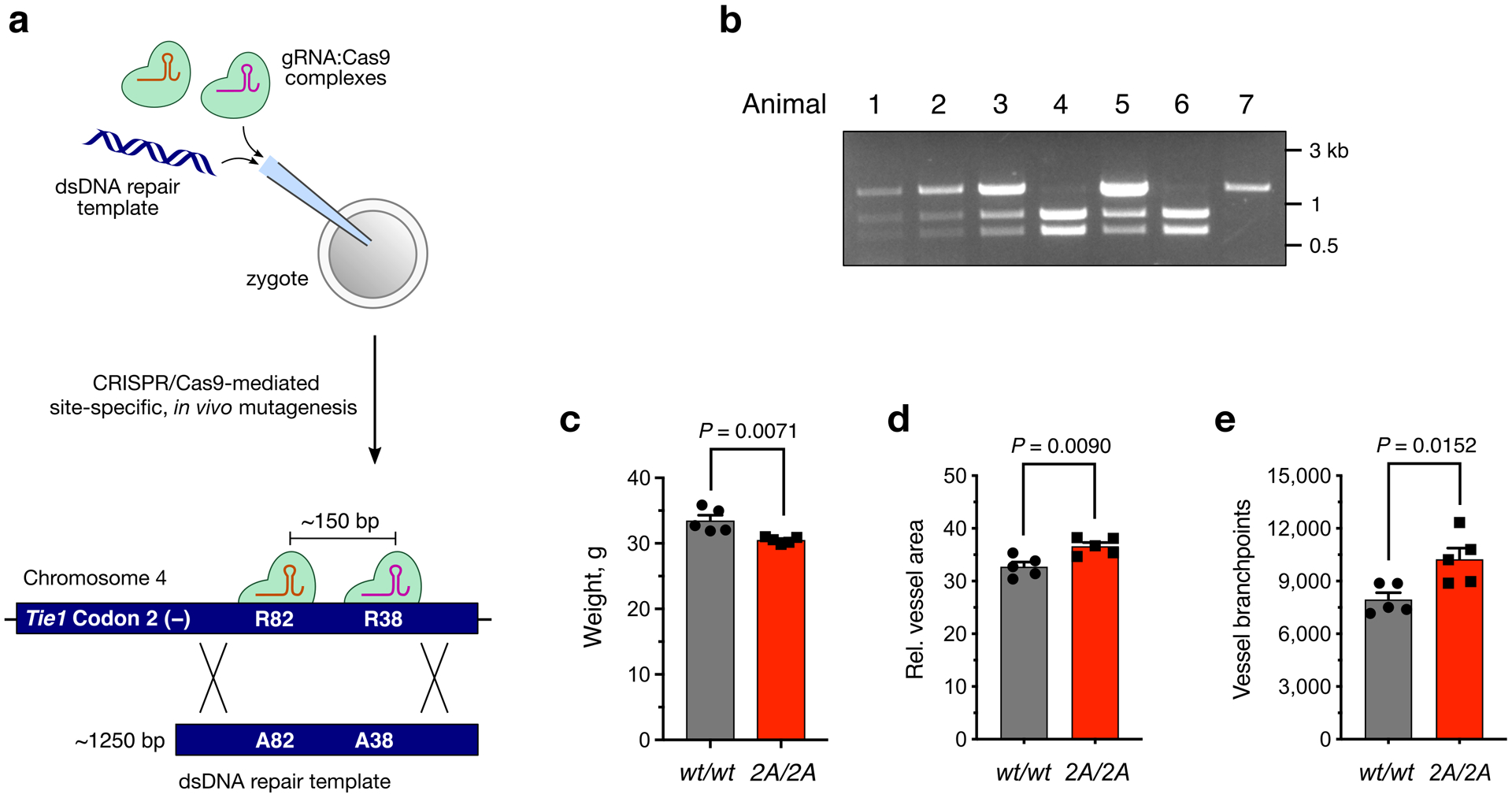
(a) Schematic of the homology-directed repair method used to generate the Tie1-2A mouse line incorporating R38A and R82A mutations into the endogenous murine Tie1 gene. (b) Representative genotyping results from a Tie12A/wt × Tie12A/wt breeding pair after the Tie1 locus was amplified by PCR and digested with StuI. Animal 7 is Tie1wt/wt, animals 1, 2, 3, and 5 are Tie12A/wt, and animals 4 and 6 are Tie12A/2A. (c) Quantification of weight differences between Tie12A/2A (2A/2A) and wild-type (wt/wt) 4-month-old, male littermates, n = 5 per genotype. (d,e) Quantification of relative vessel area and branchpoints from retinal samples described in Fig. 6, n = 5 per genotype. Data represent mean ± s.e.m., unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test.
