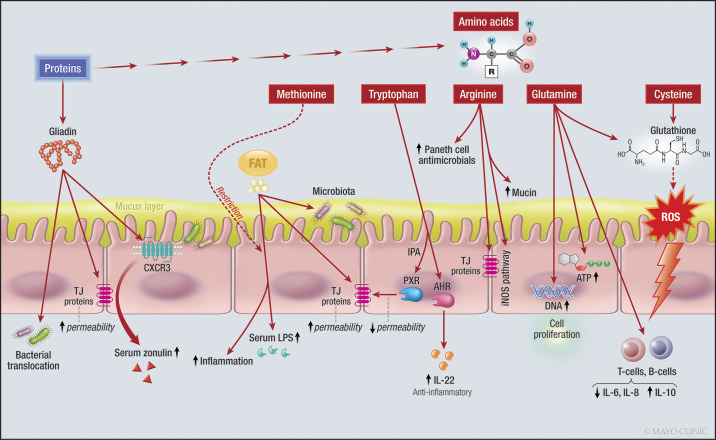
Fig. 3.
Effects of fat, proteins and amino acids on the intestinal barrier. Note the effect of amino acids on different intracellular signaling pathways and enzymes, and the effect of gliadin on CXCR3 and TJ proteins. IL-22, interleukin-22, LPS, lipopolysaccharides, TJ, tight junction, ATP, adenosine triphosphate, DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, CXCR3, chemokine receptor CXCR3; ROS, reactive oxygen species; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; PXR, pregnane X receptor; AHR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor. One sided arrow shows activation, while dashed arrow shows inhibitory effects.