Fig. 1. In vitro and in vivo characterization of transcellular and transvascular (BBB) penetration of cationic lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles loaded with siRNA.
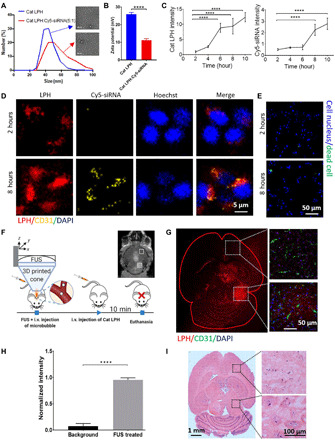
(A) Size distribution and morphology of the cationic LPH and LPH:Cy5-siRNA nanoparticles. (B) Surface charge of the cationic (Cat) LPH and LPH:Cy5-siRNA. P values were determined by unpaired t test. (C) Quantification of the LPH and Cy5-siRNA uptake by GL261 glioma cells using fluorescence microscopy. P values were determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). (D) In vitro cellular uptake kinetics of the cationic LPH:Cy5-siRNA into GL261 glioma cells. (E) Live and dead cell staining at 2 and 8 hours after LPH:Cy5-siRNA exposure. (F) In vivo experimental protocol for the delivery of cationic LPH in the brain of healthy, immunocompetent mice. Inset: Representative contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR image after MB-FUS. i.v., intravenous. (G) Representative fluorescent microscopy data of LPH extravasation in the brain of healthy mouse at 10 min after LPH administration for non-FUS region (top) and FUS-treated region (bottom). (H) Quantification of the LPH extravasation in non–FUS-treated region and FUS-treated region 10 min after treatment (12-fold; P < 0.0001, unpaired t test). (I) Representative H&E staining images at 10 min after LPH administration. Plots show means ± SEM (N = 3). ****P ≤ 0.0001.
