Fig. 3. GBM-promoting transcription factors preferentially engage tumor-enriched super-enhancers.
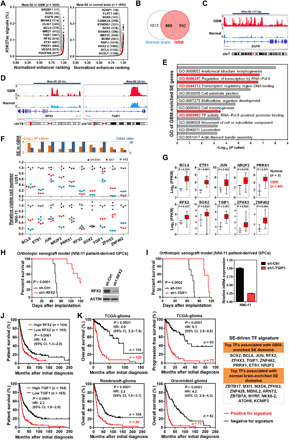
(A) Relative rank of stitched H3K27ac ChIP-seq signals in GBM (cohort 1) and normal brain tissues. Representative meta-SE–associated genes and their rankings in parentheses are highlighted. (B) Venn diagram showing common and sample type–specific meta-SE–associated genes in GBM and normal brain tissues. (C and D) Differential deposition of H3K27ac signals across regulatory regions of EGFR, RFX2, and TGIF1. (E) Ontological analysis of GBM-enriched SE genes. (F) Association of GBM-enriched SE domains with TFs and effect of shRNA-mediated silencing of top SE-associated TFs on cell viability of U251 GBM cells and NNI-11 GBM-propagating cells. (G) Elevated expression of TFs driven by tumor-enriched SEs in GBM samples (cohort 1). Student’s t test (two tailed) was applied. Boxplots represent the 25th and 75th percentiles, with midlines indicating the median values and whiskers extended to the lowest/highest values. (H and I) Effect of shRNA-mediated silencing of either RFX2 (n = 8) or TGIF1 (n = 7) in NNI-11 cells on survival of recipient mice with intracranial xenografts. Before intracranial implantation, Western blot and qPCR analyses were used to verify effective silencing of RFX2 and TGIF1, respectively. (J) Prognostic potentials of RFX2 and TGIF1 in Rembrandt cohort of glioma patients. (K) Prognostic potentials of an SE-driven TF signature in three independent cohorts of glioma patients. Log-rank test is applied in (H) to (K). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
