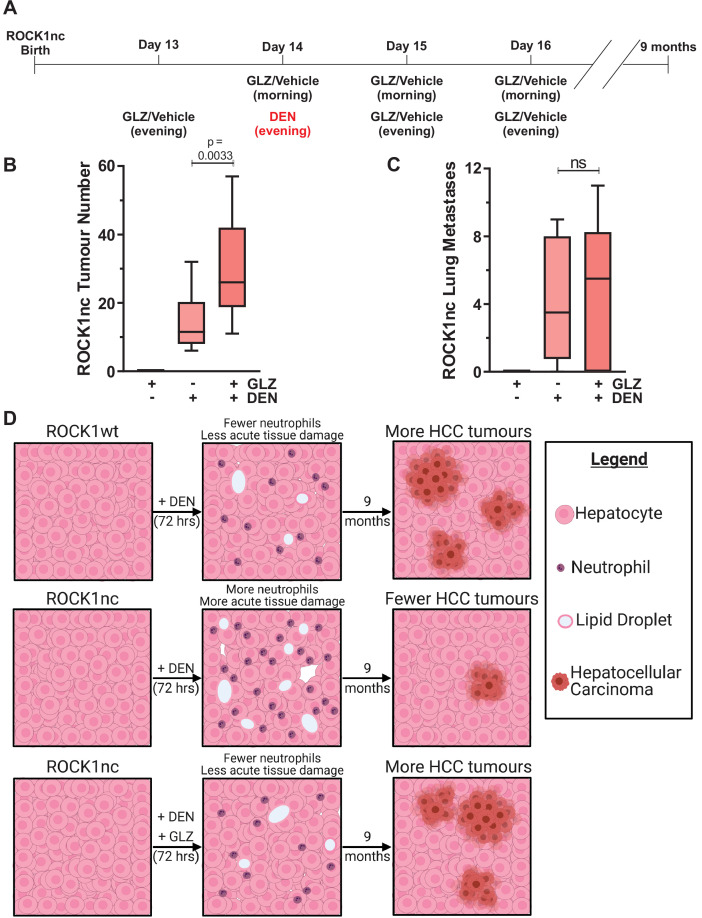
Figure 8. Glycyrrhizin (GLZ) increases diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced liver tumour number in ROCK1nc mice.
(A) Timeline of the DEN-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and GLZ treatment protocol. (B) The number of liver tumours in ROCK1nc mice 9 months after treatment with GLZ alone (n = 10 mice) or after HCC initiation with DEN alone (n = 14 mice) or with GLZ (n = 10 mice). Boxes indicate upper and lower quartiles and median, whiskers indicate 5–95% percentiles, pairwise Student’s t-test as indicated. (C) Numbers of lung metastases in ROCK1nc mice 9 months after treatment with GLZ alone (n = 10 mice) or after HCC initiation with DEN alone (n = 14 mice) or with GLZ (n = 10 mice). Boxes indicate upper and lower quartiles and median, whiskers indicate 5–95% percentiles, pairwise Student’s t-test as indicated; ns: not significant. (D) Schematic diagram depicting how acute acting neutrophils influence tumour development. ROCK1wt mice had fewer recruited neutrophils and less tissue damage than ROCK1nc mice 3 days after equivalent DEN treatment. The healthier ROCK1wt liver tissue enabled more DEN-mutated hepatocytes to initiate the HCC tumours that were observed 9 months later. Following GLZ administration, ROCK1nc mice resembled ROCK1wt mice with fewer neutrophils and less tissue damage acutely, and more HCC tumours 9 months later. Figure created with BioRender.com.