Figure 2.
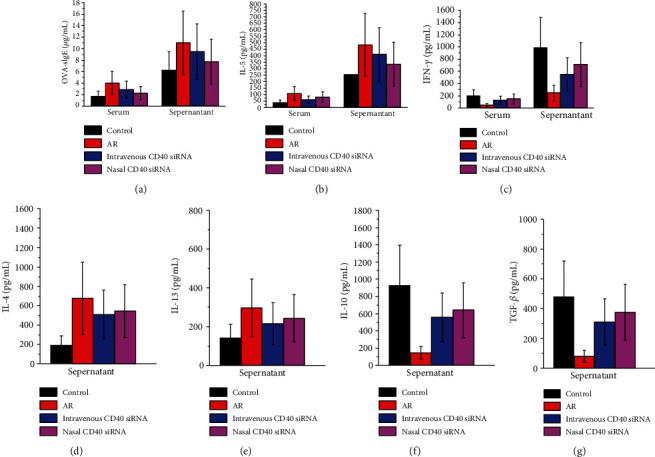
(a) Serum and supernatant levels of OVA-sIgE were measured by ELISA. AR mice produced significantly more OVA-sIgE than control. OVA-sIgE level in mice treated with CD40 siRNA was lower than AR mice. Mice treated nasally with CD40 siRNA produced significantly less OVA-sIgE than mice given intravenously CD40 siRNA. (b) Serum and supernatant levels of IL-5 were measured by ELISA. AR mice produced significantly more IL-5 than control. IL-5 level in mice treated with CD40 siRNA was lower than AR mice. (c) Serum and supernatant levels of IFN-γ were measured by ELISA. AR mice produced significantly less IFN-γ than control. IFN-γ level in mice treated with CD40 siRNA was higher than AR mice. Mice treated nasally with CD40 siRNA produced significantly more IFN-γ than mice given intravenously CD40 siRNA. (d) Supernatant levels of IL-4 were measured by ELISA. AR mice produced significantly more IL-4 than control. IL-4 level in mice treated with CD40 siRNA was lower than AR mice. (e) Supernatant levels of IL-13 were measured by ELISA. AR mice produced significantly more IL-13 than control. IL-13 level in mice treated with CD40 siRNA was lower than AR mice. (f) Supernatant levels of IL-10 were measured by ELISA. AR mice produced significantly less IL-10 than control. IL-10 level in mice treated with CD40 siRNA was higher than AR mice. (g) Supernatant levels of TGF-β were measured by ELISA. AR mice produced significantly less TGF-β than control. TGF-β level in mice treated with CD40 siRNA was higher than AR mice. P values <0.05 were considered as significance.
