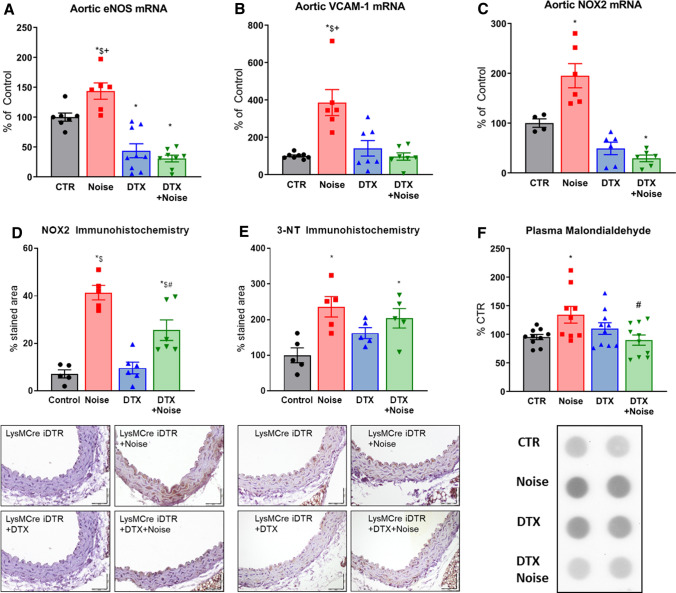
Fig. 5.
Ablation protects from noise-induced increases in mRNA expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), oxidative stress and inflammatory parameters and plasma oxidative stress markers. Noise increased mRNA expression of eNOS, VCAM-1, NOX-2 expression (a–c). Ablation of LysM+ cells reduced eNOS and NOX-2 mRNA (a, c) below control levels, while the expression of VCAM-1 (b) remained at baseline. d, e Protein expression of NOX-2 and abundance of 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT)-positive proteins in the aorta as determined by immunohistochemistry were increased by noise and partially normalized by DTX treatment. Representative immunohistochemical images are shown below the quantification and the scale bars reflect 50 µm. f Oxidative stress marker, malondialdehyde assessed by dot blot analysis, was increased by noise and normalized by LysM+ cell ablation. Data points are measurements from pools of 3–4 aortas (a–c), number of animals (d, e) or pools of plasma from 2–4 animals per data point (f); one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (a–f). *P < 0.05 vs. Control; #P < 0.05 vs. Noise; $P < 0.05 vs. DTX, +P < 0.05 vs. DTX + Noise