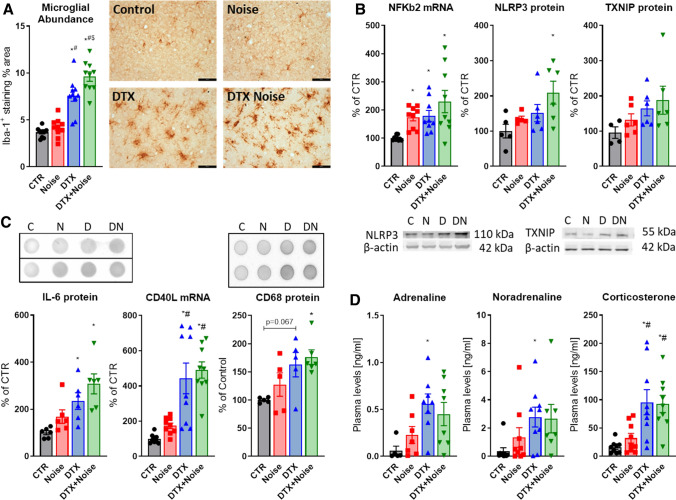
Fig. 7.
Diphtheria toxin treatment of LysMCreiDTR mice fails to prevent neuroinflammation in the brain and stress responses by noise. a Iba-1 staining revealed no ablation of microglia in LysMCreiDTR mice. Interestingly, Iba-1+ cells and % of Iba-1+ area were even increased in both DTX-treated groups and further aggravated by noise exposure. Representative immunohistochemical images are shown besides the quantification and the scale bar reflects 50 µm. b Presence of a neuroinflammatory phenotype was supported by higher levels of NFkB mRNA as well as NLRP3 and TXNIP protein expression in brains of LysMCreiDTR mice with DTX treatment, which was exacerbated by noise exposure. Representative western blot images are shown below the densitometric quantification. c IL-6 and CD68 protein as well as CD40L mRNA expression were slightly increased by noise and further exacerbated in the DTX groups. Representative dot blot images are shown above the densitometric quantification. d Neuronal stress response and release of stress hormones adrenaline, noradrenaline and corticosterone were also higher in the LysMCreiDTR mice with DTX treatment. Data points are measurements from individual animals; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test or respective non-parametric test (a–d). *P < 0.05 vs. Control; #P < 0.05 vs. Noise; $P < 0.05 vs. DTX