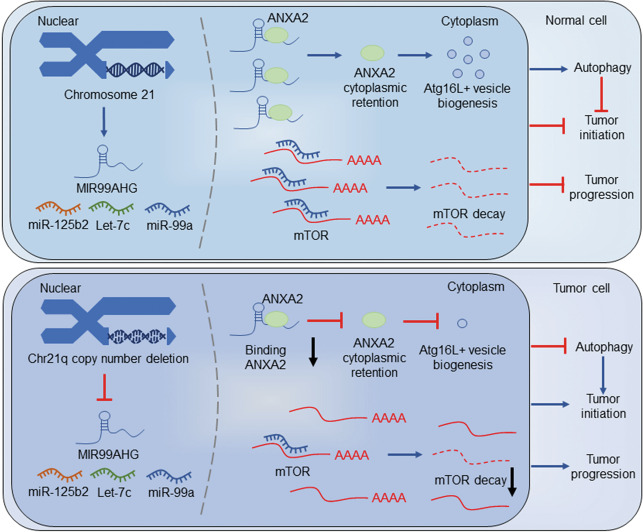
Fig. 8. Schematic diagram of how MIR99AHG promotes autophagy and inhibits the progression of LUAD.
In tumor cells, copy number deletion of 21q leads to the low expression of MIR99AHG and the miR-99a/let-7c/miR-125b2 cluster. MIR99AHG binds to ANXA2 to sustain cytoplasmic retention of ANXA2 which accelerates the biogenesis of ATG16L+ vesicles, and MIR99AHG-derived miR-99a targets mTOR, thus promoting autophagy and repressing the progression of LUAD. MIR99AHG/miR-99a-mediated autophagy enhanced the inhibition effect of these antitumor genes on the LUAD biogenesis, while loss of the autophagy promoted the tumor initiation induced by deficiency of these tumor suppressors.