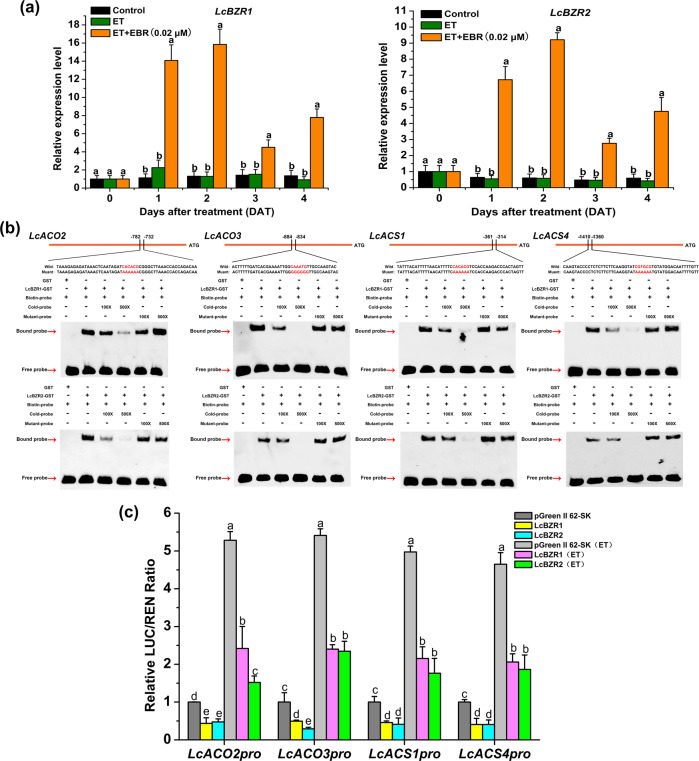
Fig. 3. Binding of LcBZR1/2 to the LcACO2/3 and LcACS1/4 promoters to repress their expression.
a LcBZR1/2 were induced in the fruitlet abscission zone (FAZ) under ET + EBR treatment. b Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) showing the binding ability of LcBZR1/2 with the promoters of LcACO2/3 and LcACS1/4 in vitro. Sequences of both the mutant and wild-type probes are presented on the top. Shifted bands, indicating the formation of DNA-protein complexes, are marked by arrows. ‘+’ and ‘-’ represent presence and absence, respectively. 100× and 500× indicate increasing amounts of mutant or unlabeled probes used for testing the specificity of binding and competition. Probes without biotin labels were loaded as unlabeled competitors. GST protein alone was used as the negative control. c LcBZR1/2 suppressed the expression of LcACO2/3 and LcACS1/4 in vivo, as shown by transient dual-luciferase reporter assays. Both effector and reporter vectors were cotransformed into tobacco leaves. After incubation with or without ethylene (ET, 50 µl L−1) for 48 h the ratio of LUC to REN was detected. Error bars indicate SEs from six replicates. Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).