Fig. 3.
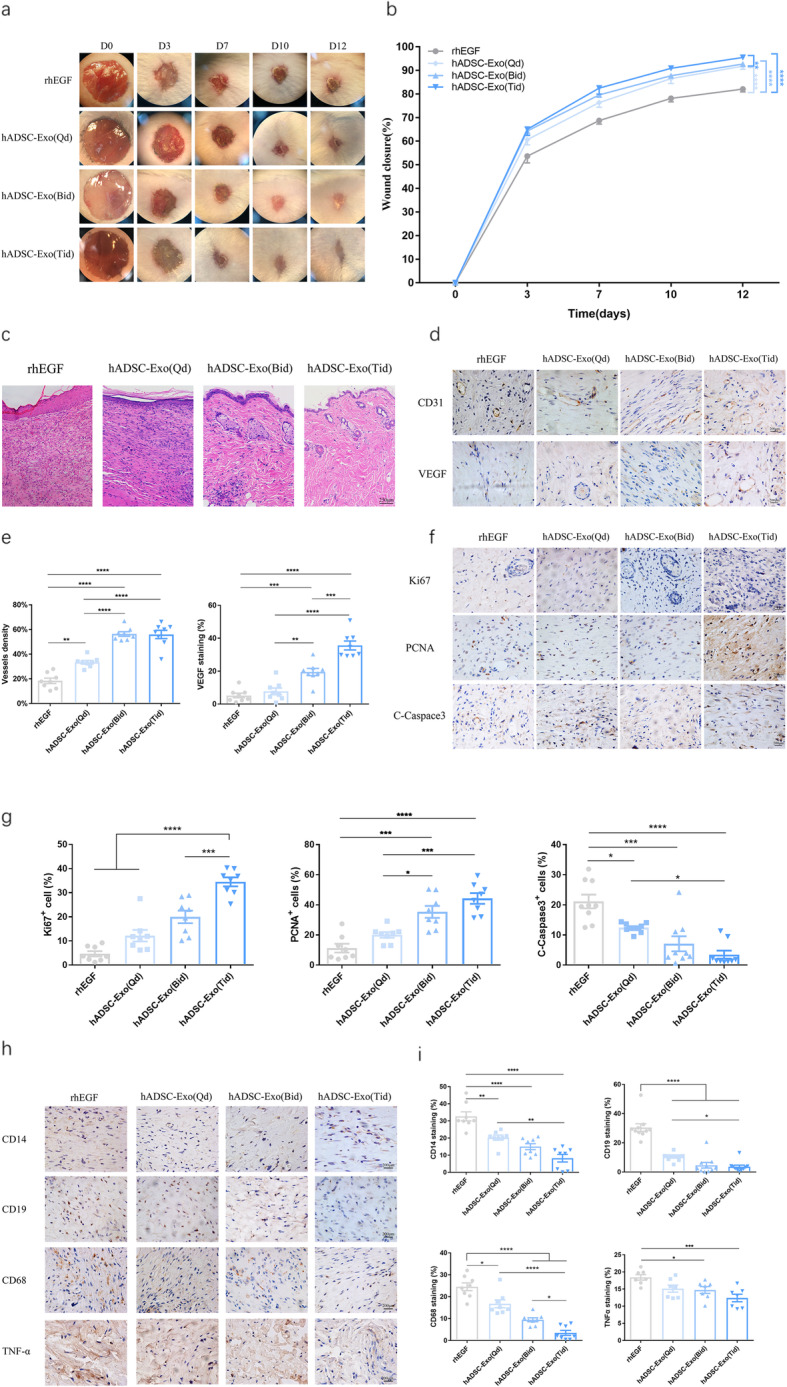
Effect of hADSC-Exo treatment on wound healing in vivo mouse model in a dose-dependent manner. a Representative photographs of full-thickness excisional wounds treated with hADSC-Exo (Qd), hADSC-Exo (Bid), and hADSC-Exo (Tid). b Quantitative analysis of wound healing in each group. c Histological structure of wounded skin in different groups. Scale bar = 250 μm. d Representative photographs of CD31 and VEGF immunostaining. Scale bar = 200 μm. e Quantitative analysis of the number of mature blood vessels. f Representative photographs of Ki67, PCNA, and C-Caspase3 immunostaining. Scale bar = 200 μm. g Ki67, PCNA, and C-Caspase3 expression of IHC-positive staining analyzed by mean percentage (±SEM). h Representative photographs of CD14, CD19, CD68, MPO, and TNF-alpha immunostaining. Scale bar = 200 μm. i Quantification of CD14+, CD19+, CD68+, and TNF-alpha+ IHC stained tissues. The rhEGF was used as a positive control. Results are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean; n = 8 for each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 vs vehicle control group
