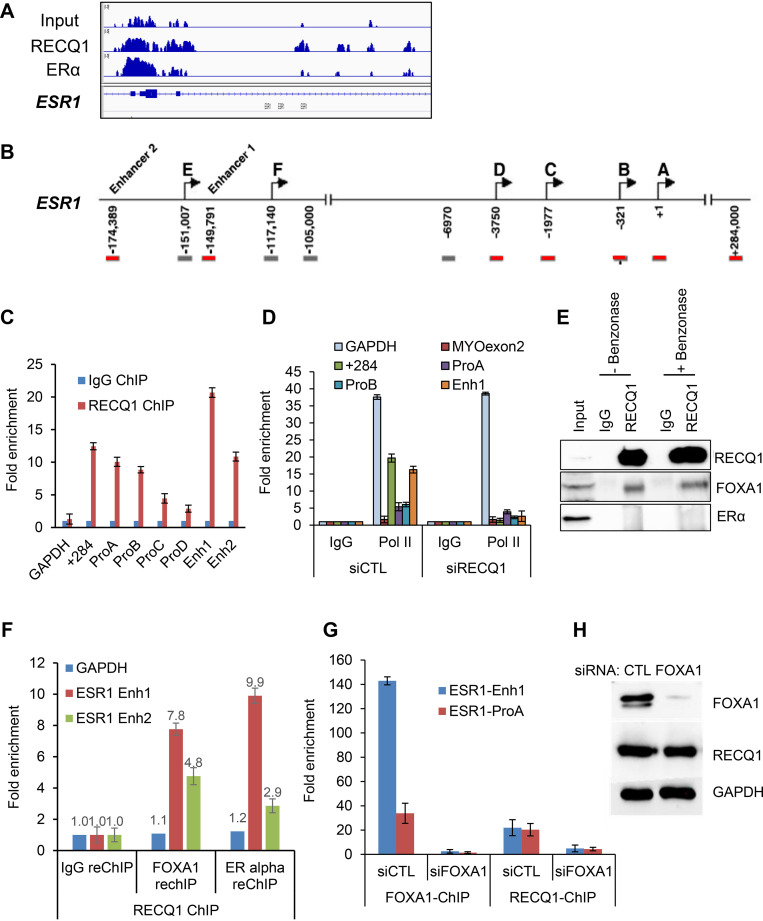
FIG 5.
RECQ1 binding to the ESR1 locus is FOXA1-dependent. (A) An IGV snapshot of RECQ1 and ERα ChIP-seq peaks is shown for the ESR1 locus. (B) Location of primers used to amplify promoter and enhancer regions of ESR1 is shown. (C and D) ChIP-qPCR shows strong enrichment of RECQ1 at specific promoter and enhancer regions of ESR1. (C) MCF7 cells were transfected with control (siCTL) siRNA or RECQ1 siRNAs (siRECQ1) for 48 h, and ChIP-qPCR was performed using a control IgG antibody or RECQ1 antibody. (D) The data show that RECQ1 knockdown in MCF7 cells results in reduced RNA Pol II occupancy at specific promoter and enhancer regions. (E) RECQ1 associates with FOXA1 but not ERα protein, as assessed by immunoblotting after IP from MCF7 whole-cell extracts using a control IgG antibody or RECQ1 antibody. The RECQ-FOXA1 interaction is not DNA or RNA dependent because it is not sensitive to benzonase. (F) ChIP/re-ChIP assays show the colocalization of RECQ1, FOXA1, and ERα at ESR1 regulatory regions. ChIP/re-ChIP assays in MCF7 cells with RECQ1 as first ChIP, followed by a re-ChIP with either IgG or antibody against FOXA1 or ERα. Re-ChIP DNA was quantified by qPCR at ESR1 enhancer 1 and enhancer 2. (G) ChIP-qPCR was performed from MCF7 cells transfected with siCTL or FOXA1 siRNAs (siFOXA1) using a FOXA1 antibody or RECQ1 antibody. The data show that the binding of RECQ1 to a region in the ESR1 promoter and enhancer is abolished upon knockdown of FOXA1 with siRNAs in MCF7 cells. As expected, binding of FOXA1 to these regions was lost upon knockdown of FOXA1 in siRNAs in MCF7 cells. (H) Immunoblotting was performed from MCF7 whole-cell lysates prepared after transfection of MCF7 cells with control (CTL) or FOXA1 siRNAs for 48 h. Immunoblotting was used to confirm knockdown of FOXA1 in the ChIP-qPCR experiment in panel F; FOXA1 knockdown did not affect RECQ1 protein levels. GAPDH was used as a loading control.