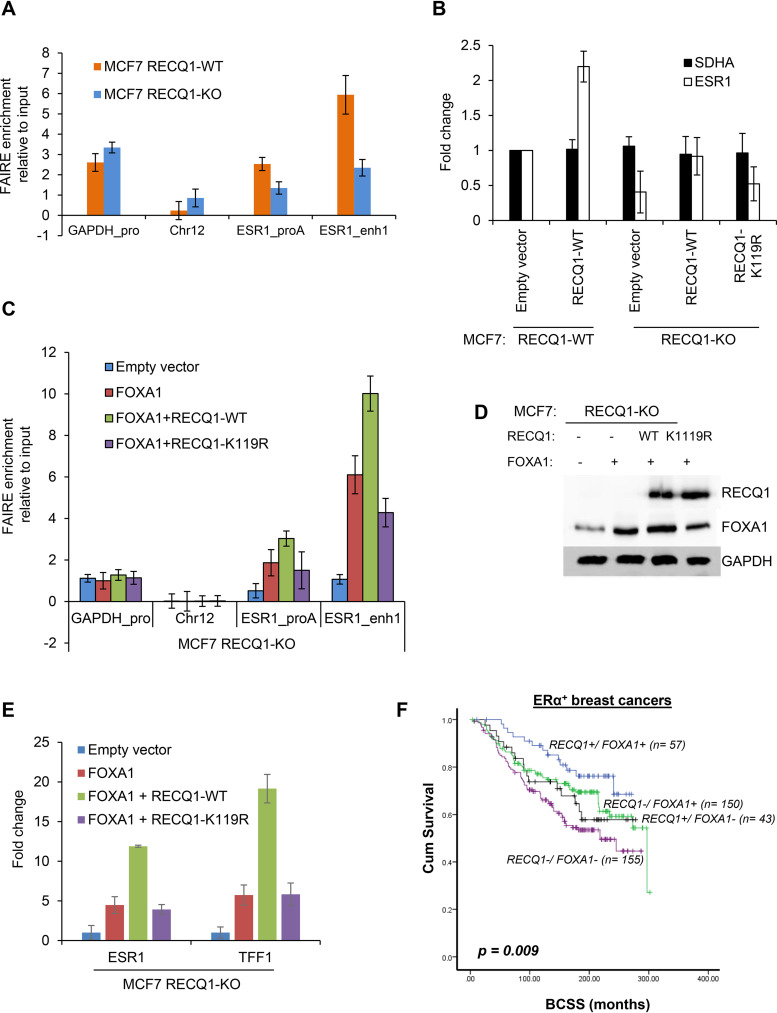
FIG 6.
RECQ1 helicase cooperates with FOXA1 to regulate ESR1 expression. (A) FAIRE assays were performed using MCF7 RECQ1-WT or isogenic MCF7 RECQ1-KO cells, and the changes in chromatin accessibility at an ESR1 promoter (ESR1_proA) region and an ESR1 enhancer (ESR1_enh1) were assessed by FAIRE-qPCR. The promoter regions of GAPDH and a heterochromatin region in chromosome 12 were used as positive and negative controls, respectively, for open chromatin. (B) RT-qPCR assays for ESR1 and the housekeeping gene SDHA were performed with MCF7 RECQ1-WT transfected with empty vector or a vector that expresses WT RECQ1 (RECQ1-WT) for 48 h. In parallel, RT-qPCR assays for ESR1 and the housekeeping gene SDHA were performed with MCF7 RECQ1-KO cells transfected with empty vector or a vector that expresses WT RECQ1 (RECQ1-WT) or helicase-dead RECQ1 mutant (RECQ1-K119R) for 48 h. The fold change refers to the fold change in gene expression normalized to GAPDH. (C to E) MCF7 RECQ1-KO cells were transfected with empty vector, FOXA1-expressing vector (FOXA1), or FOXA1-expressing vector in combination with RECQ1-expressing vectors that were RECQ1 WT (RECQ1-WT) or helicase-dead RECQ1 mutant (RECQ1-K119R). (C) Changes in chromatin accessibility at ESR1 regulatory regions in these cells were determined by FAIRE-qPCR. An increase in FAIRE enrichments by FOXA1 was further enhanced by cotransfection with a helicase-active wild-type RECQ1. The relative enrichment of the FAIRE signal normalized to input chromatin is shown for the promoter of GAPDH (positive control), a heterochromatin region on chromosome 12 (negative control), and the ESR1 promoter A and enhancer 1. (D) The effect on FOXA1 and RECQ1 protein was determined by immunoblotting using GAPDH as a loading control. (E) The effect on ESR1 or TFF1 expression was determined by RT-qPCR at 48 h after transfection. Fold change refers to fold change in gene expression normalized to GAPDH. (F) Kaplan-Meier curves for RECQ1/FOXA1 coexpression and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) in ERα+ breast cancers.