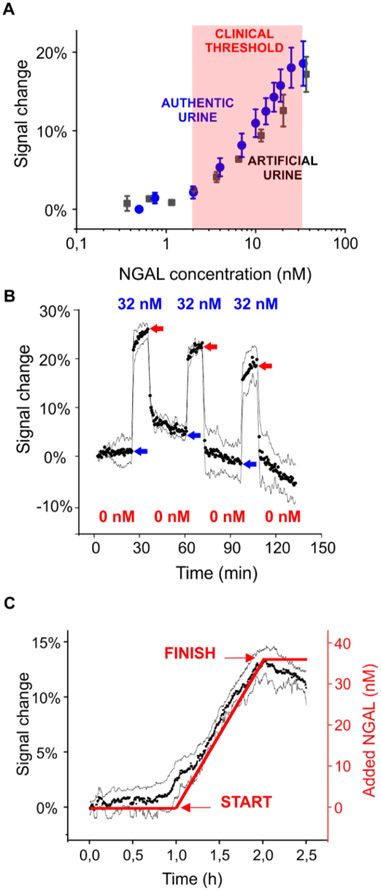
Figure 2.
Real-time monitoring of clinically relevant threshold levels of NGAL in urine. (A) Threshold NGAL level indicative of diseases has variously been reported30 to be from 2 to 32 nM. The useful dynamic range of our sensor spans these concentrations in both artificial urine and authentic human urine. The data represent the average signals and the standard deviations of at least three independently fabricated sensors, illustrating the excellent sensor-to-sensor reproducibility we achieve even with these hand-held devices. (B) The sensor responds promptly to the addition (blue arrows) and removal (red arrows) of NGAL. Shown are three cycles of addition (32 nM) and removal of NGAL over 2 h. (C) The sensor easily monitors a continuous rise in (spiked) NGAL that mimics the profile expected for acute renal injury.