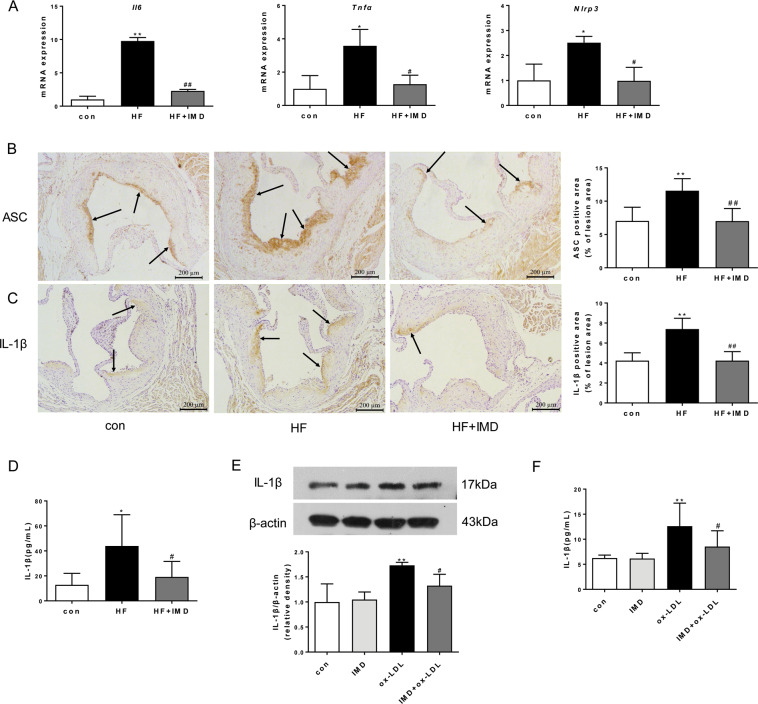
Fig. 6. IMD1-53 inhibited apoptosis-triggered inflammasome in advanced lesional macrophage.
A–C Eight-week-old male ApoE−/− were fed a standard chow diet (con) or a high-fat diet (HFD) for 16 weeks. After 10 weeks of HFD feeding, ApoE–/– mice received either PBS or intermedin1-53 (IMD1-53) during the left 6 weeks of high-fat diet feeding. Quantitative real-time PCR of interleukin6 (IL6), tumor necrosis factor α (Tnfα), and Nlrp3 mRNA expression (A). Results are relative to the GAPDH level (n = 3). Representative images and quantification data of apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing CARD (ASC) (B) and IL-1β (C) immunohistochemical staining at the aortic root of mice from con, HF, and HF + IMD. Black arrows indicate the area stained positively for ASC or IL-1β. Scale bars, 200 μm. n = 6. D Plasma IL-1β level was measured. n = 6. Data are mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 compared with con, #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 compared with HF group; one-way ANOVA. E Western blot analysis of protein expression of IL-1β in macrophages treated with PBS, IMD1-53, ox-LDL and IMD1-53 + ox-LDL. β-actin was a control for protein loading. Results are representative of four experiments. Densitometric analysis of protein levels is shown as a ratio to β-actin. n = 4. F IL-1β in the cell culture supernatant was also measured. n = 5. Data are mean ± SD. **P < 0.01 compared with con, #P < 0.05 compared with the ox-LDL group; one-way ANOVA.