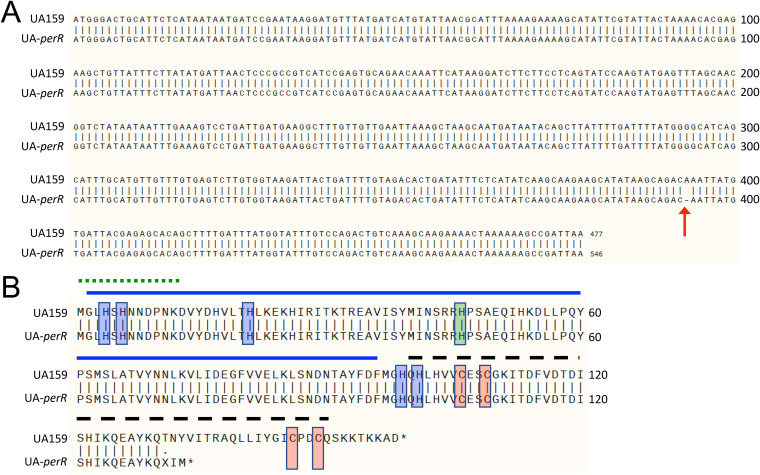
FIG 1.
Whole genomic sequencing reveals a perR SNP that results in a prematurely truncated protein in S. mutans UA159. (A) Alignment of nucleotide sequences of perR from UA159 from the NCBI (perR+) and UA-perR (perR SNP strain). The arrow at base 393 indicates a 1-bp deletion in the sequence of UA-perR. (B) Alignment of amino acid sequences of PerR from UA159 and UA-perR, indicating a premature termination of the latter. Red shading indicates zinc-coordinating cysteine residues critical for PerR function. Blue shading indicates histidine residues involved in binding of a regulatory Fe molecule. Green shading indicates a histidine residue believed to be important in DNA binding. The solid blue line indicates the N-terminal DNA-binding domain. The dashed black line indicates the C-terminal dimerization domain. The dotted green line indicates an N-terminal extension unique to PerR members of the Fur family and conserved among streptococci. Structural domains were based on homologies to those described in PerR of S. pyogenes, whose crystal structure has been solved (22).