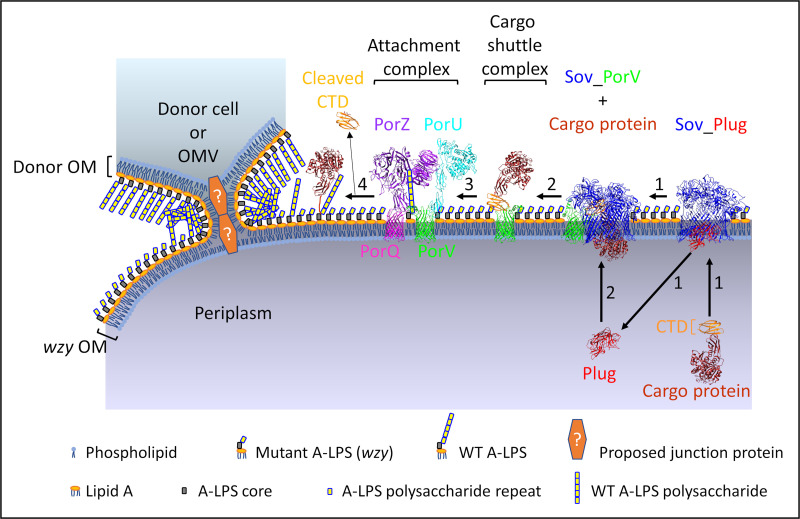
FIG 9.
Proposed model for LPS exchange and A-LPS complementation in P. gingivalis. Proposed model for complementation of the wzy LPS mutant by LPS exchange with donor cell or OMV possessing WT unconjugated A-LPS. The OM of wzy cell fuses with the OM of the donor cell or OMV by forming a tight junction via an unknown OM adhesin or junction protein. Donor WT A-LPS then transfers to the OM of wzy cell to provide functional A-LPS for the T9SS attachment complex. Step 1, PorV (green) plugs the side opening of the Sov (blue) pore, and the plug protein (red) exits from the pore, allowing the cargo protein to enter the Sov pore and interact with the PorV loops that are inside the Sov channel (39). Step 2, the cargo shuttle complex comprising PorV bound to the CTD (orange) of the cargo protein (brown) is released from Sov, and the plug protein reenters from the periplasm. Step 3, the cargo shuttle complex interacts with the attachment complex (PorV-PorU-PorQ-PorZ) that is primed via PorZ (purple) with WT A-LPS derived from the donor cell/OMV, allowing the CTD of the cargo protein to be cleaved by PorU (cyan) and the new C terminus of the cargo protein to be conjugated to the WT A-LPS for anchorage to the OM and release of cleaved CTD (step 4) (7, 8, 38). If WT A-LPS is not present, the CTD of the cargo protein is still cleaved by PorU but is not conjugated to A-LPS, and it is released from the cell surface. The second LPS of P. gingivalis, O-LPS, is not represented. Structures for Sov_Plug (PDB ID: 6H3J) and Sov_PorV (PDB ID: 6H3I) complexes were determined by cryo-electron microscopy (39). The crystal structures for mature RgpB (PDB ID: 1CVR) (90) and RgpB CTD (PDB ID: 5AG9) (91) were used for the cargo protein. PorZ is from the crystal structure (PDB ID: 5m11) (43). PorV (green) and PorQ (magenta) β-barrel structures are from Phyre2 models using amino acid sequences without N-terminal signal peptides. The PorU structure is a Phyre2 model without a signal peptide or domain A (7). Attachment and cargo shuttle complexes are depicted based on composition of complexes and subcomplexes (16, 38).