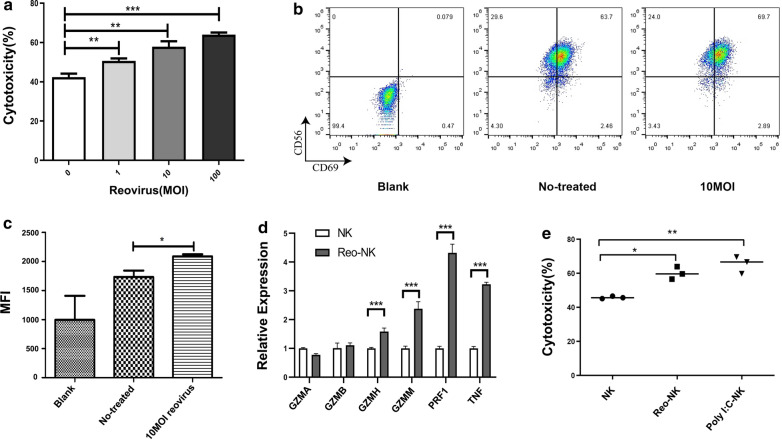
Fig. 1.
Effects of reovirus on NK cells. a NK cells were incubated in the absence or presence of 1, 10, or 100 MOI reovirus at 37℃ for 12 h. DLD-1 cells were used as target cells. Cytotoxic activity was measured at 4 h by CCK-8 assays performed on target cells at an E:T ratio of 5:1. All samples were assayed in triplicate and these data are representative of three independent experiments.(**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). b Representative flow cytometry plots showing the expression of CD69 on NK cells stimulated or not with 10 MOI reovirus for 12 h. c Compiled data (mean ± SEM)from three independent experiments showing mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for CD69, d qPCR evaluation of the relative expression of GZMA, GZMB, GZMH, GZMM, PRF1, and TNF in NK cells after 12 h exposure to 10 MOI reovirus or medium alone (control; NK).qPCR experiments were performed twice with three technical replicates per sample. Data are means ± SD (***p < 0.001). e NK cells were incubated at 1 × 106 cells/mL for 12 h in medium alone or 10 MOI reovirus; NK cells were transfected with 1 μg/mL Poly(I:C) by Lipofectamine and also cultured for 12 h. The NK cells stimulated under the various conditions were then co-cultured with DLD-1 cells for 4 h at a 5:1 E:T ratio. NK cell cytotoxicity was determined by CCK-8 assay. Data shown above are from a representative assay selected from three independent experiments. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01)