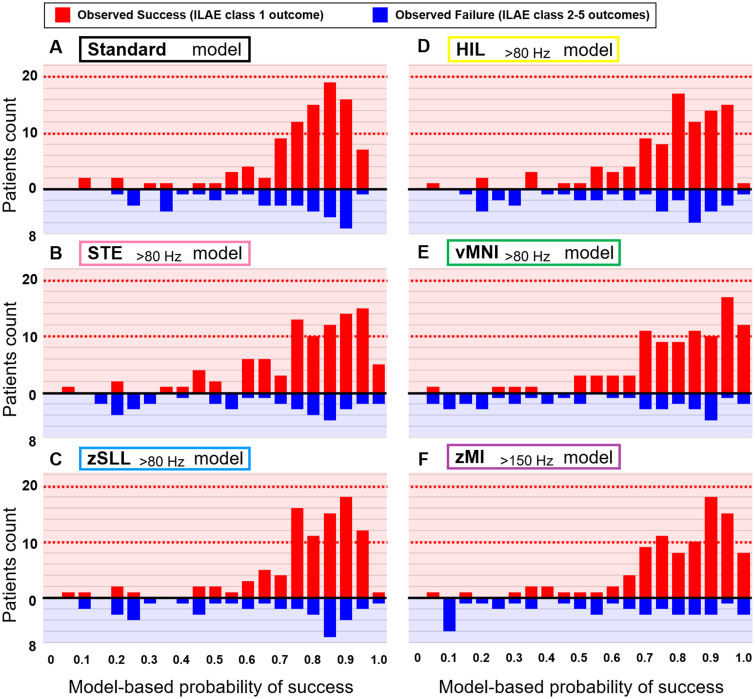
Figure 6.
Agreement between the model-based prediction and the observed frequency of surgical success. X-axis: Model-based probability of surgical success for a given patient; each model was cross-validated by the leave-one-out procedure. Red bar: Number of patients achieving the ILAE class 1 outcome. Blue bar: The class 2 outcome or worse. (A) The standard model anticipated that 55 patients would achieve surgical success with a probability of greater than 0.8. Thereby, 42 out of these 55 patients (76%) indeed achieved surgical success. The standard model anticipated that 5 patients would achieve surgical success with a probability of smaller than 0.2. However, four out of these five patients (80%) still achieved surgical success. (B) The STE>80 Hz model. (C) The zSLL>80 Hz model. (D) The HIL>80 Hz model. (E) The vMNI>80 Hz model. (F) The zMI>150 Hz model anticipated that 61 patients would achieve surgical success with a probability of greater than 0.8. Indeed, 51 out of these 61 patients (84%) achieved surgical success. The zMI>150 Hz model anticipated that 10 patients would achieve surgical success with a probability of smaller than 0.2. Indeed, only two out of these 10 patients (20%) achieved surgical success.