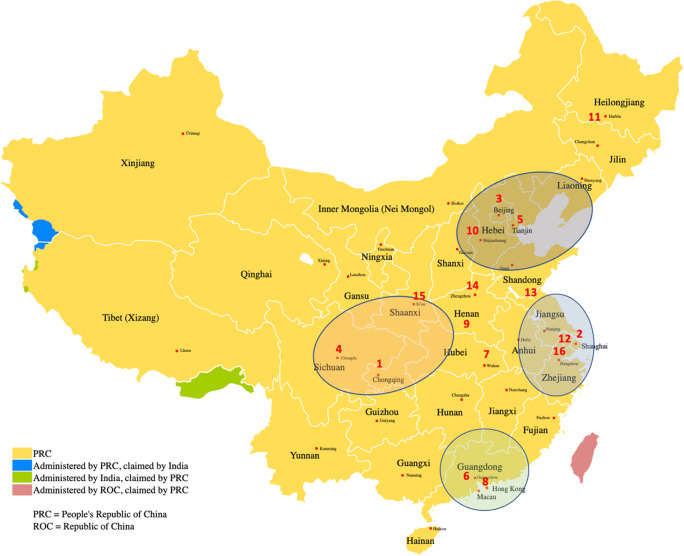
Fig. 1.
Map of China and four biobusiness clusters (map from Wikimedia China administrative, ASDFGH). As of 2020, China had 16 megacities with over 10 million inhabitants. These were, ranked by population (number is also position on map), (1) Chongqing, (2) Shanghai, (3) Beijing, (4) Chengdu, (5) Tianjin, (6) Guangzhou, (7) Wuhan, (8) Shenzhen, (9) Nanyang, (10) Shijiazhuang, (11) Harbin, (12) Suzhou, (13) Linyi, (14) Zhengzhou, (15) Xi’an, and (16) Hangzhou. Much of China’s pharmaceutical research and industry is located in 4 biobusiness clusters shown here as bubbles: the northeastern cluster (Liaoning, Hebei, Beijing, Tianjin, and Shandong), the eastern cluster (Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Shanghai), the southern cluster (Guangdong and Hong Kong), and the western cluster (Sichuan, Shaanxi, Hubei and Chongqing). In these 4 clusters lived 53% of the Chinese population and generated 63% of China’s GDP