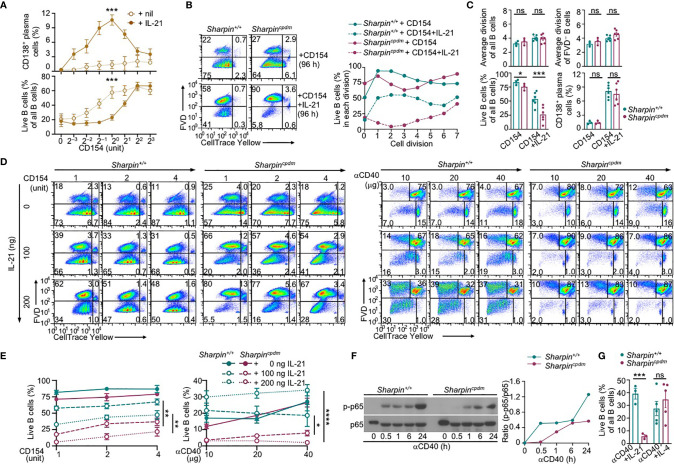
Figure 5.
SHARPIN deficiency exacerbates IL-21-induced death in CD154-stimulated B cells. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of plasma cell differentiation and B cells viability in C57 B cells stimulated with different doses of CD154, as indicated, in the absence or presence of IL-21 for 96 h (n=4, mean and s.e.m.; data at 1 unit of CD154 were analyzed for statistical differences between Sharpin+/+ and Sharpincpdm B cells). (B, C) Flow cytometry analysis of proliferation, survival, and plasma cell differentiation of Sharpin+/+ and Sharpincpdm B cells stimulated with CD154 or CD154 plus IL-21 for 96 (h) Division-linked B cell viability is depicted in (B), representative of four independent experiments) and average divisions, live B cell proportions, and CD138+ plasma cell proportions were depicted in (C). (D, E) Flow cytometry analysis of proliferation, survival of Sharpin+/+ and Sharpincpdm B cells stimulated with CD154 (left panels) or αCD40 (right panels) at indicated doses in the presence of different doses of IL-21 for 96 h (n=3, mean and s.e.m.; data at 4 units of CD154 or 40 μg of αCD40 were analyzed for statistical differences between Sharpin+/+ and Sharpincpdm B cells). (F) Immunoblotting of phosphorylated p65 and total p65 protein levels in Sharpin+/+ and Sharpincpdm B cells after stimulation by αCD40 for the indicated time. Representative of two independent experiments. (G) Live cell proportions in Sharpin+/+ and Sharpincpdm B cells stimulated with αCD40 plus IL-21 or IL-4 for 96 (h) *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; t-test.