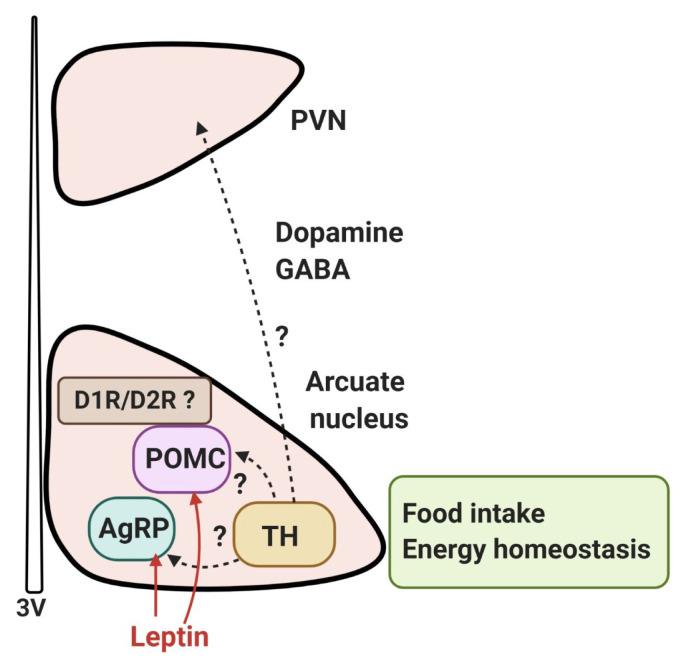
Fig. 2.
Dopaminergic control of food intake in the hypothalamus. Dopamine neurons (tyrosine-hydroxylase [TH]-positive) are present throughout the hypothalamus, particularly in the arcuate nucleus and dorsomedial nucleus. It has been reported that dopamine neurons of the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus colocalize with the vesicular GABA transporter and corelease GABA; these cells project to the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and communicate with leptin-responsive neurons, such as pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons or agouti-related peptide (AgRP) neurons. [50,51]. The effect of hypothalamic dopamine signaling is mediated mostly by D1R and D2R, and it appears that the D1R and D2R are located on POMC neurons, co-localized with leptin receptors in the arcuate nucleus, raising the possibility that dopamine signaling in the hypothalamus may be involved in the leptin signaling-mediated network to contribute to hypothalamic control of energy homeostasis. However, the details of the dopaminergic circuits in the hypothalamus are currently unknown. 3V, third ventricle.