Table 2.
Examples of some terpenes that are primarily produced by plants and their antiviral activity and mechanism of action
| Volatile terpen compound | Used technique | Test influenza strain | Mechanism of action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
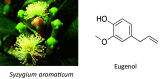
|
In vitro | H1N1- 4 strains, H3N2-2 strains, H9N2-2 strains, H5N1-1 strain |
1. Disrupts the viral reproduction and the subsequent hypercytokinemia 2. Inhibition or reduction in the interaction of NA and HA proteins 3. Prolongs cell proliferation |
[56, 57] |

|
In vitro, in vivo |
H1N1-2 strains, H3N2-2 strains, Influenza B virus-1 |
Interferes with the transcription machinery and attachment of the virus proteins prior and during the infectious process | [58, 59] |
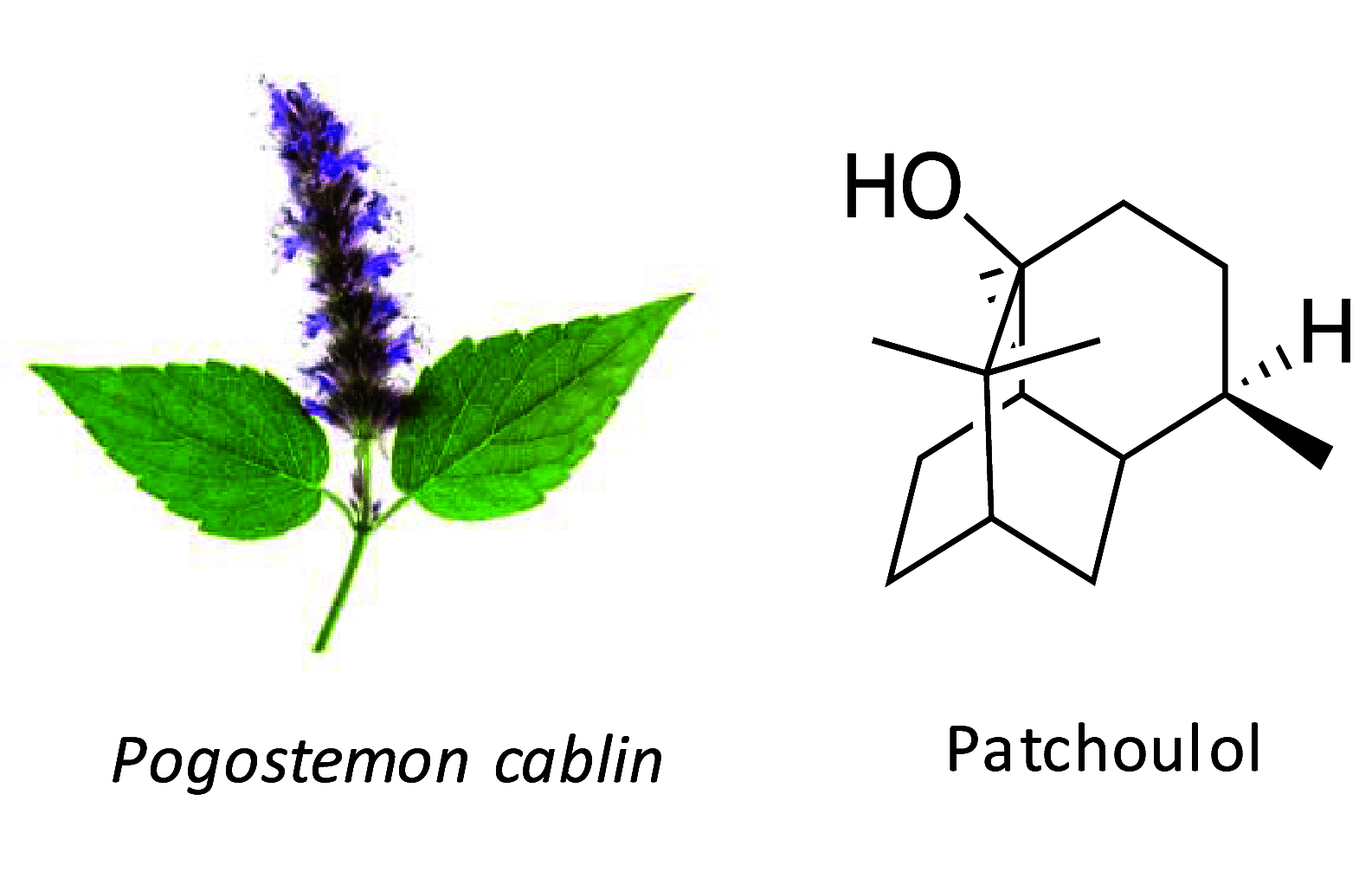
|
In vitro, in vivo |
H1N1-2 strains, H2N2-1 strain, H3N2-1strain, Influenza B virus-1 strain |
1. Disrupts the viral reproduction and the subsequent hypercytokinemia 2. Inhibition or reduction in the interaction of NA and HA proteins |
[59–62] |

|
In vitro | H3N2-1 strain, H1N1-1 strain | Interacts with the translation process of the viral genome to reduce the amount of the produced mRNA | [59, 63] |
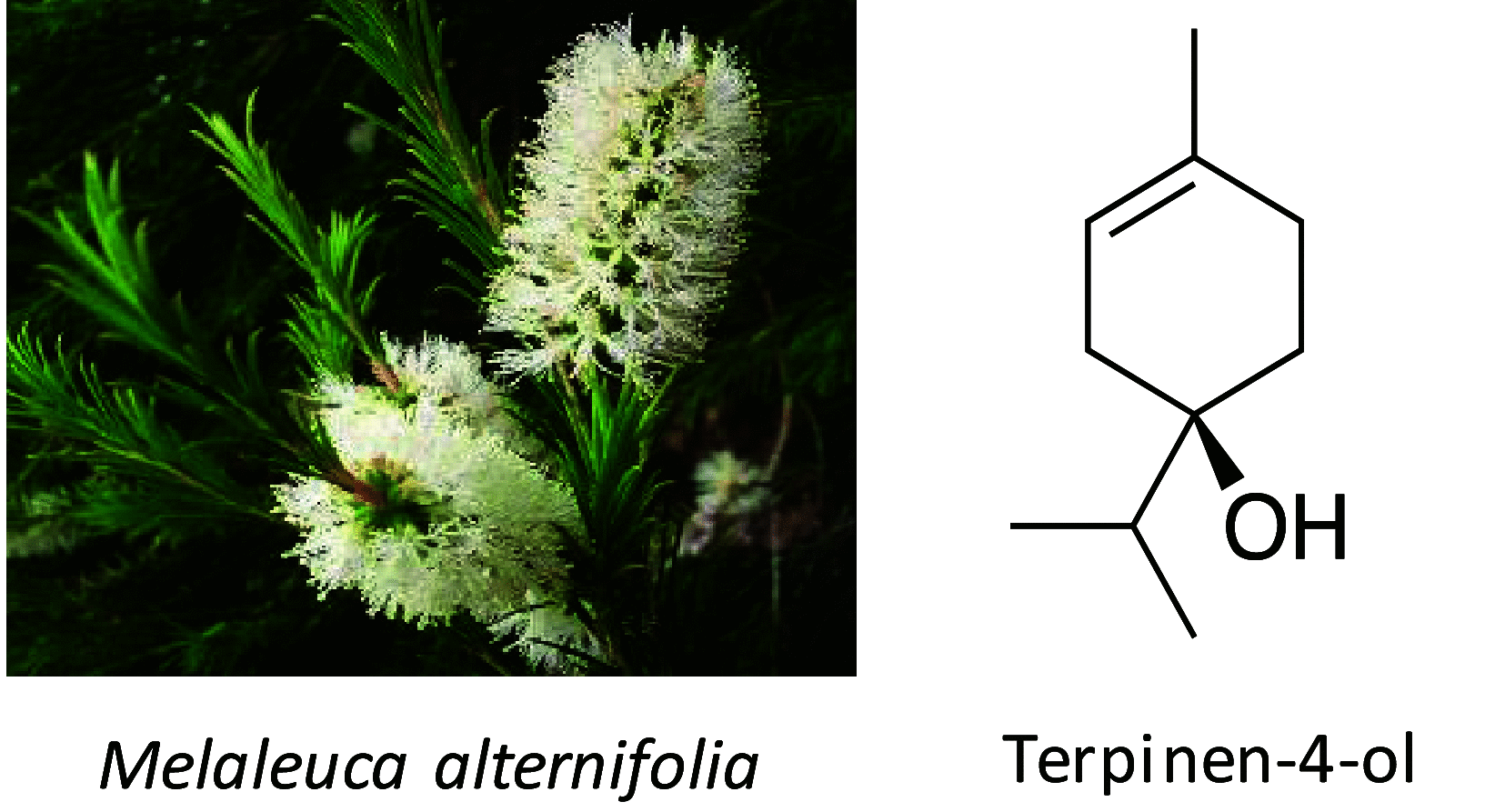
|
In vitro | H1N1-1 strain | Causes reduction in cell transportation networking during the acidification process | [64–66] |

|
In vitro | H1N1-1 strain | Causes reduction in cell transportation networking during the acidification process | [65, 66] |

|
In vitro | H1N1- 1 strain | Causes reduction in cell transportation networking during the acidification process | [65, 66] |
