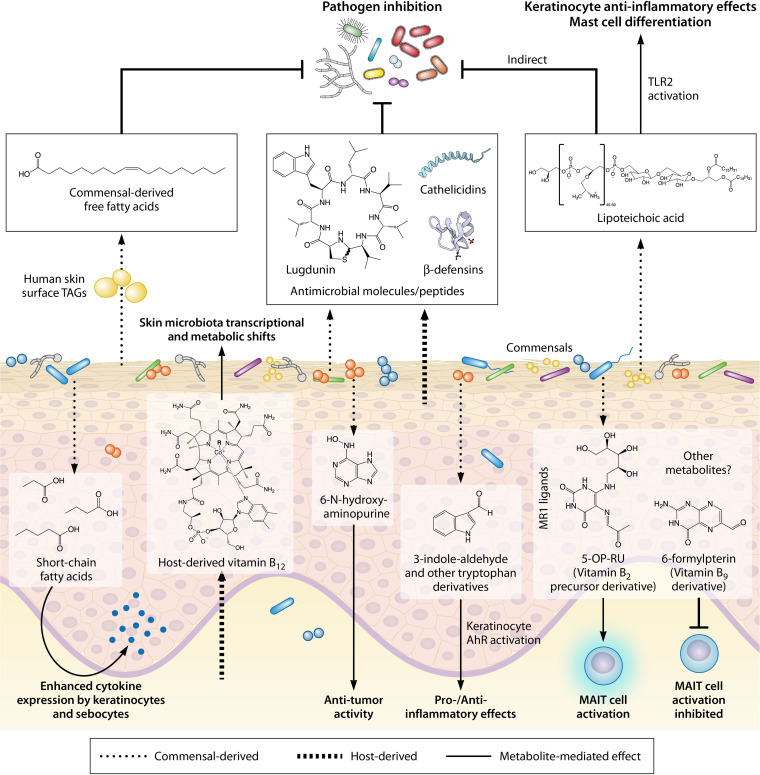
FIG 2.
Metabolite-mediated interactions in the skin. The skin microbiota, which colonizes the skin and its appendages both epidermally and subepidermally, produces chemically diverse metabolites, which may be synthesized de novo or metabolized from host-derived molecules. These metabolites confer numerous benefits for the host, including pathogen inhibition, immune education and homeostasis, or even anti-tumor activity. However, under certain conditions, microbial products may promote an inflammatory response. Further, metabolites derived from the host can modulate commensal metabolism, demonstrating the bi-directionality of host-microbiota interactions on the skin.