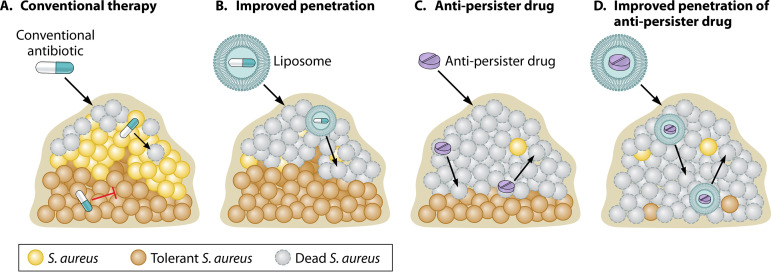
FIG 2.
A combined approach for improving antibiotic efficacy against S. aureus biofilms. (A) Biofilms display remarkable tolerance to antibiotics. Susceptible cells at the biofilm periphery die (dead S. aureus), while less metabolically active cells within the biofilm are tolerant to conventional antibiotics (tolerant S. aureus). Failure to eradicate the biofilm leads to relapse in infection following removal of the antibiotic. (B) Encapsulating drugs in liposomes will improve penetration of some conventional antibiotics that do not penetrate well through the biofilm matrix. This strategy is limited, as it does not improve killing of antibiotic-tolerant persister cells (tolerant S. aureus) and leads to relapse. (C) Targeting biofilms with antibiotics which kill persister cells (antipersister drug) improves efficacy, but if drug penetration is impeded into the biofilm, some cells will remain viable following drug treatment and lead to relapse. (D) Encapsulating antipersister drugs in liposomes improves penetration of drugs that are active against persister cells. Combining strategies to improve antibiotic efficacy against biofilms will improve the chances of eradicating all cells within a biofilm and prevent relapse of infection following removal of the antibiotic. Schematic credit: created with BioRender and modified by Patrick Lane, ScEYEnce Studios.