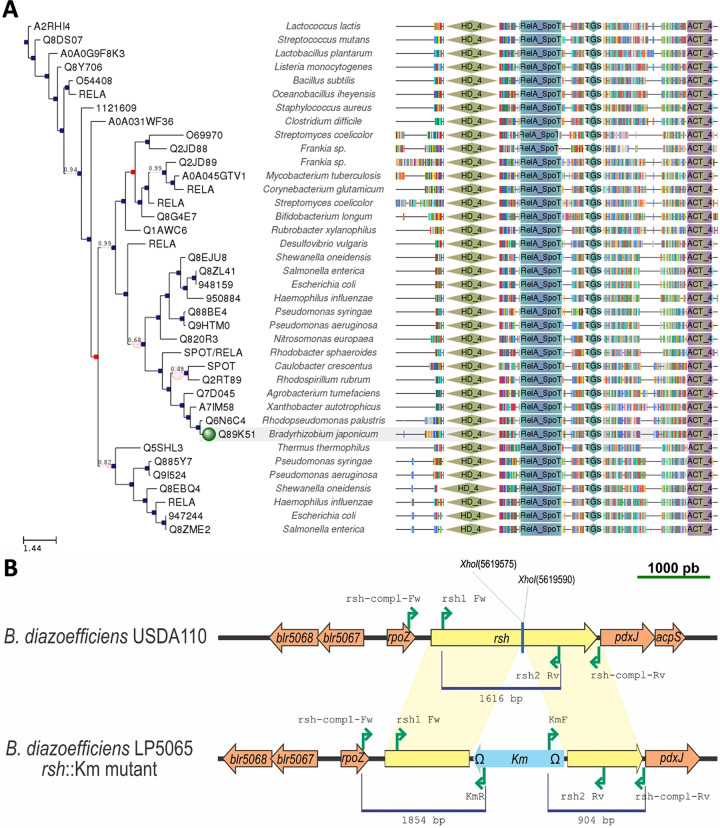
FIG 1.
Scheme of rsh and its mutant derivative. (A) Domain structure of various rsh, relA or spoT analogs from different species, obtained from Phylome DB-Tree Explorer on 16 August 2019. Blue squares indicate speciation events; red squares indicate duplication events. The green dot indicates the target sequence. Since the species name was not updated in this database, it still appears as “Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110,” but it should be referred to as “Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA 110.” The following domains (according to Pfam) are shown: the metal-dependent phosphohydrolase (HD_4 [green diamonds]); the characteristic RelA/SpoT protein domain (RelA_SpoT [blue-green rectangles]); ThrRS, GTPase, and SpoT, which is a possible nucleotide-binding region (TGS [blue diamonds]); and the ACT domain, which binds to amino acids and regulates associated enzyme domains (ACT_4 [violet and yellow rectangles]). (B) Comparison of the wild type (upper row) and rsh insertional mutant (lower row) from B. diazoefficiens. The positions and directions of the primers used to obtain and validate the mutation are indicated by green arrows. The sizes of the fragments used for the mutation are indicated below the blue lines. The insertion occurred between the XhoI sites at bases 5619575 and 5619590 in reverse orientation.