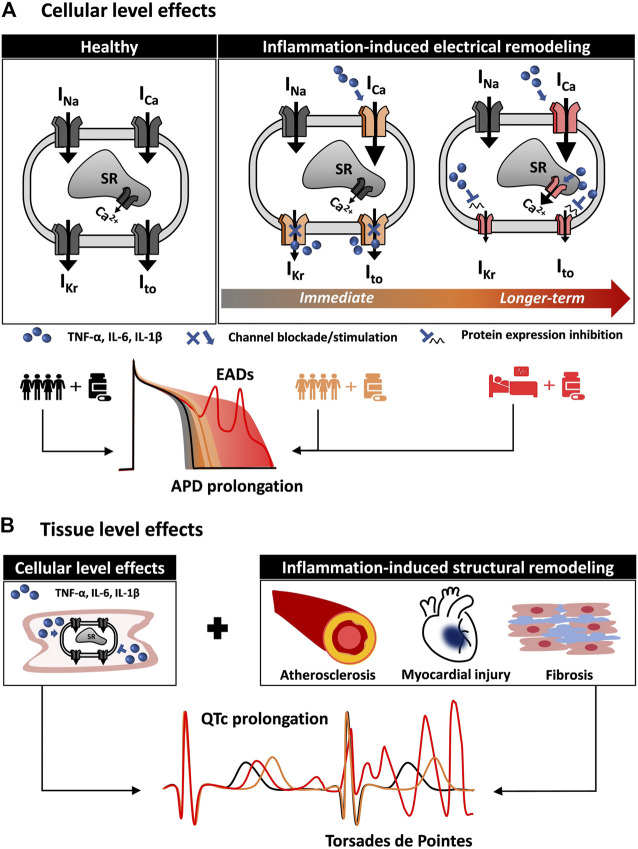
FIGURE 1.
Multiscale quantitative systems pharmacology to integrate inflammation modeling into in silico drug safety evaluation. (A) Inflammation induces cardiac electrical remodeling. Proinflammatory cytokines can alter cardiac electrophysiology by interacting directly with the cardiac ion channels. By altering the normal function (immediate effect) and expression of cardiac ion channels (longer-term effect), inflammation is a source of variability in the cardiomyocyte response to the administration of drugs. In addition to variability among healthy individuals (black line and gray shaded area), the inflammatory state (orange and red) can profoundly alter the cellular pro-arrhythmia risk metrics normally evaluated in in silico drug safety. (B) Inflammation affects cardiac tissue pro-arrhythmia risk metrics. Inflammation also contributes to cardiac structural remodeling, affecting cardiac propagation and creating a proarrhythmic substrate. Together with the effects on the single cardiomyocyte, this can result in altered (orange and red) QT interval on the ECG.