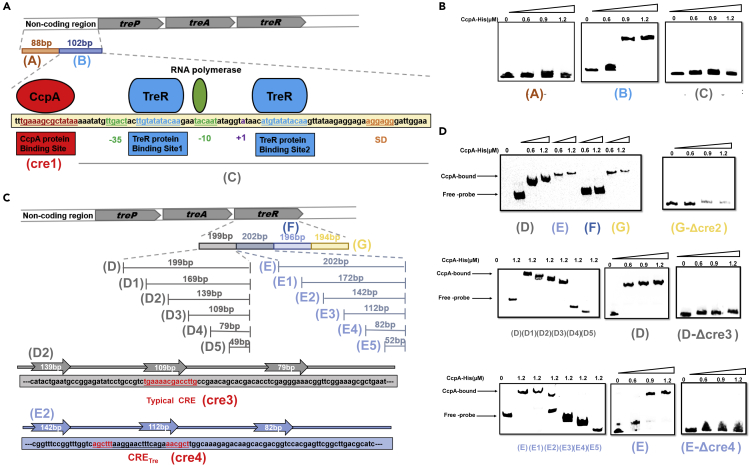
Figure 1.
Identification of CcpA binding sites in trehalose operon
(A) The non-coding region of the trehalose operon was divided into two fragments ([fragment A] and [fragment B]). The CcpA binding region is shown in red, and the TreR binding region is shown in blue. The −10 region and −35 region are shown in green. The transcription start site is shown in purple. The SD sequence is shown in orange.
(B) EMSA of CcpA protein binding to three fragments (fragment A, fragment B, and fragment C) labeled with 5′ biotin.
(C) The region of treR gene was divided into four fragments (fragment D, fragment E, fragment F, and fragment G). The fragment D of the treR gene was further divided into six fragments (fragment D, fragment D1, fragment D2, fragment D3, fragment D4, and fragment D5). The fragment E of the treR gene was further divided into six fragments (fragment E, fragment E1, fragment E2, fragment E3, fragment E4, and fragment E5). The CcpA binding site in fragment D or fragment E is shown in red.
(D) EMSA of CcpA protein binding to four fragments (fragment D, fragment E, fragment F, and fragment G) labeled with 5′ biotin, six fragments labeled with 5′ biotin (fragment D, fragment D1, fragment D2, fragment D3, fragment D4, and fragment D5) that were derived from fragment D, and six fragments labeled with 5′ biotin (fragment E, fragment E1, fragment E2, fragment E3, fragment E4, and fragment E5) that were derived from fragment E.