FIG 4.
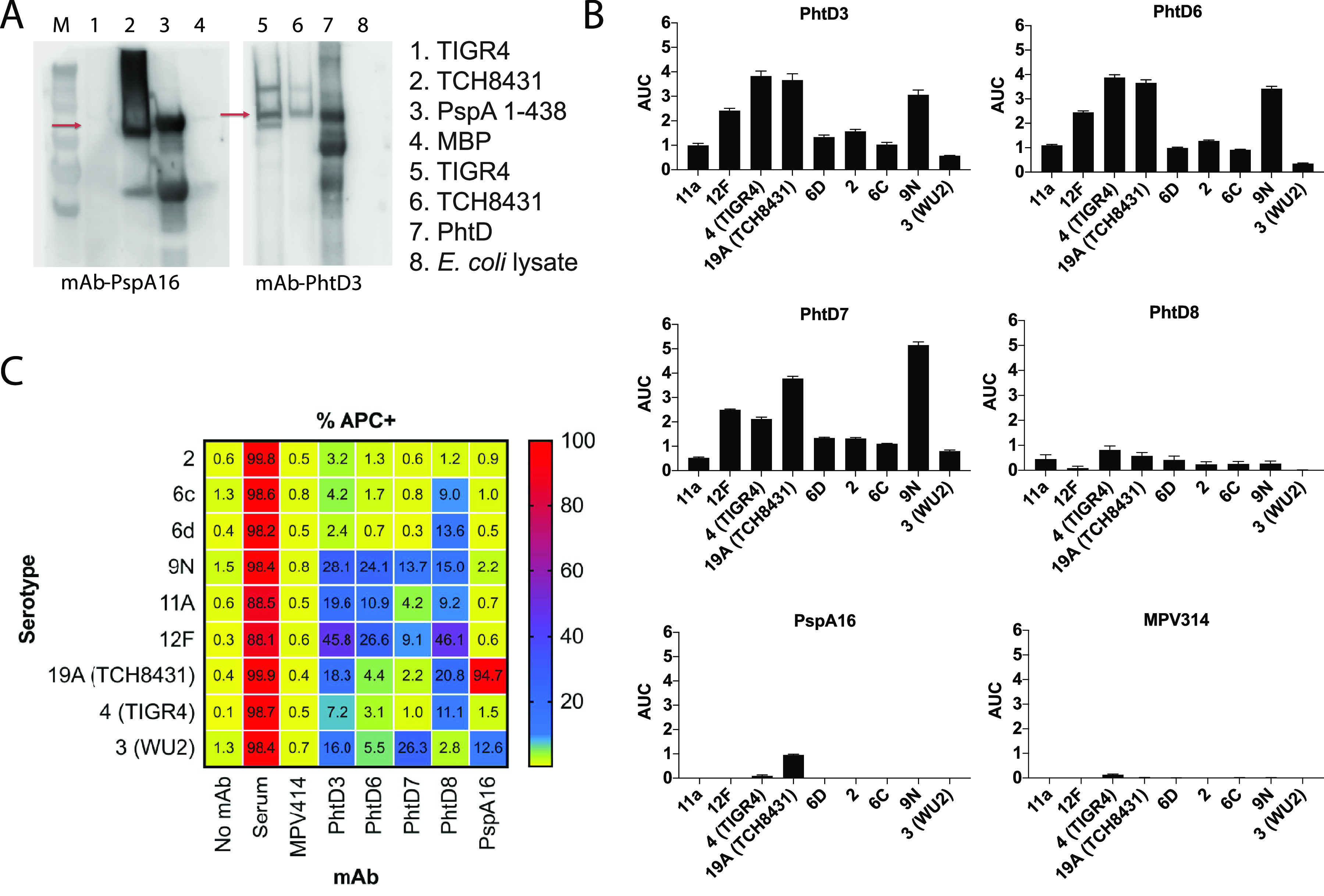
Serotype breadth of the isolated MAbs. (A) Western blot of TIGR4 and TCH8431 strains with PspA16 and PhtD3 as the primary antibodies. In the Western blot for PspA16, the PspA fragment from aa 1 to 438 fused to the MBP was used as the positive control, and MBP was used as the negative control. In the PhtD3 Western blot, recombinant PhtD was used as the positive control, and E. coli lysates were used as the negative control. (B) Area-under-the-curve (AUC) values calculated from ELISA binding curves of serially diluted MAbs against plates coated with fixed bacteria. The ELISA binding curves were the averages of four data points from one of at least two independent experiments. The baseline for the AUC calculation was set as the average of the signal for the highest concentration (20 μg/ml) of the negative control MAb MPV314. Error bars show standard errors of the AUC calculation. (C) Example gating strategy for antibody binding to bacteria. Bacteria were labeled with CFSE, and antibodies were labeled with APC. (D) Heat map and percentages for antibody binding to each pneumococcal serotype. Data are averages from 3 or 4 experiments and are the percentage of bacteria that are APC positive. MPV314 and MPV414 are human antibodies specific to the human metapneumovirus fusion protein, and these were used as negative controls.
