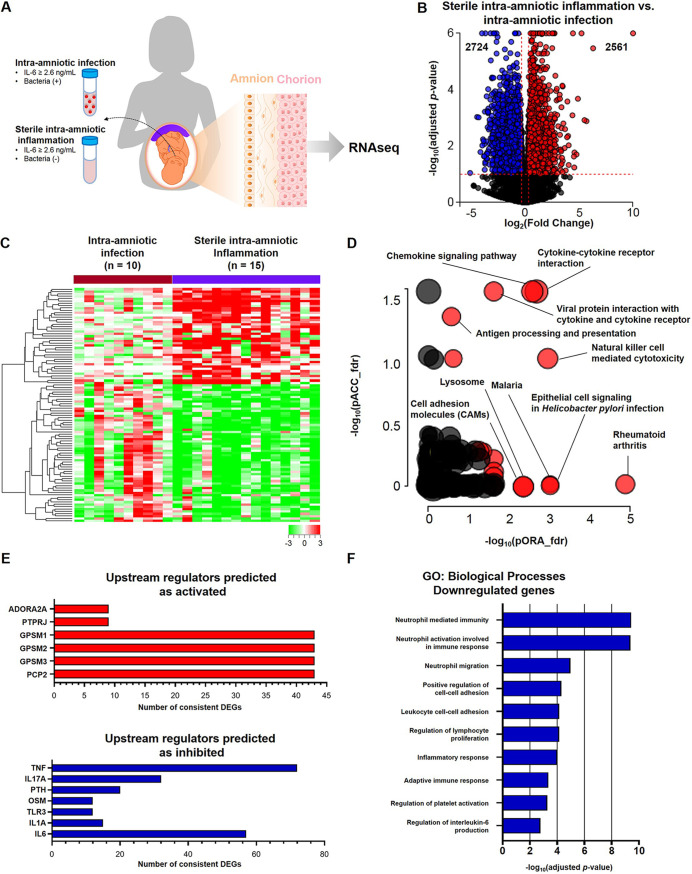
FIG 3.
RNA seq reveals distinct immune responses in the chorioamniotic membranes of women with preterm labor and sterile intra-amniotic inflammation. (A) Experimental design showing the transcriptomic comparison between the chorioamniotic membranes from women with sterile intra-amniotic inflammation (n = 15) and those with intra-amniotic infection (n = 10). (B) Volcano plot showing the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the chorioamniotic membranes from women with sterile intra-amniotic inflammation and those with intra-amniotic infection. (C) Heatmap showing the chorioamniotic membrane expression (log2 thereof after eventual adjusting for covariates and subtracting the mean in the reference group) of the top 100 DEGs ranked by magnitude of change between groups. (D) KEGG pathway impact analysis evidence plot showing gene overrepresentation evidence (pORA) and total pathway accumulation evidence (pAcc) based on differential expression between the chorioamniotic membranes from women with sterile intra-amniotic inflammation and those with intra-amniotic infection. Significantly impacted pathways are shown as red dots. (E) Predicted activated and inhibited upstream regulators of DEGs in the chorioamniotic membranes from women with sterile intra-amniotic inflammation compared to those with intra-amniotic infection. (F) Gene ontology (GO) analysis using genes significantly downregulated in the chorioamniotic membranes from women with sterile intra-amniotic inflammation compared to those with intra-amniotic infection. The top 10 most significantly enriched biological processes are shown.