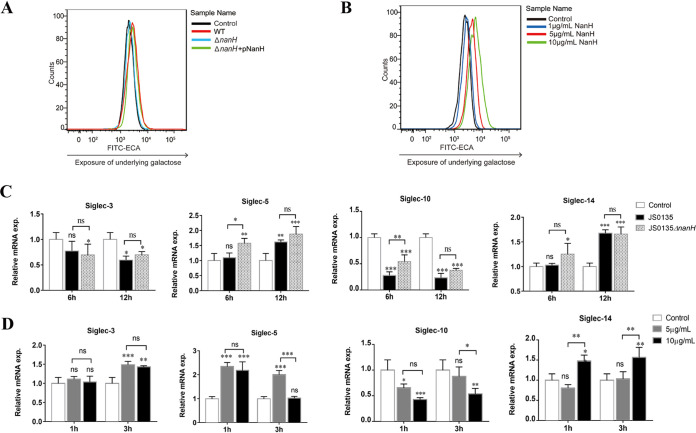
FIG 3.
Desialylation and altered Siglec expression in 3D4/21 cells upon the action of sialidase of Glaesserella parasuis. (A) The desialylation of 3D4/21 cells was detected using a flow cytometer based on exposure to underlying galactose. Cells infected with wild-type (WT) G. parasuis at a multiplicity of infection of 10 for 6 h showed more galactose exposure than the mutant (ΔnanH::kan) and complementary (ΔnanH::kan+pNanH) strains. (B) Cells treated with recombinant sialidase (rNanH) for 3 h showed desialylation in a dose-dependent manner. (C) The mRNAs for Siglec-3, -5, -10, and -14 in 3D4/21 cells infected with WT and ΔnanH::kan strains were detected using real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR). Asterisks above each pillar indicate the comparisons between control cells and cells infected with WT and ΔnanH::kan strains. Additional asterisks indicate the comparison between WT and ΔnanH::kan strains. (D) The mRNAs for Siglec-3, -14, -5, and -10 were detected in 3D4/21 cells following rNanH treatment. Asterisks above each pillar indicate comparisons between the control cells and cells treated with 5 μg/ml and 10 μg/ml rNanH. Additional asterisk indicates the comparison between 5 μg/ml and 10 μg/ml of rNanH. All qRT-PCRs were performed in three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, no significance.