FIG 4.
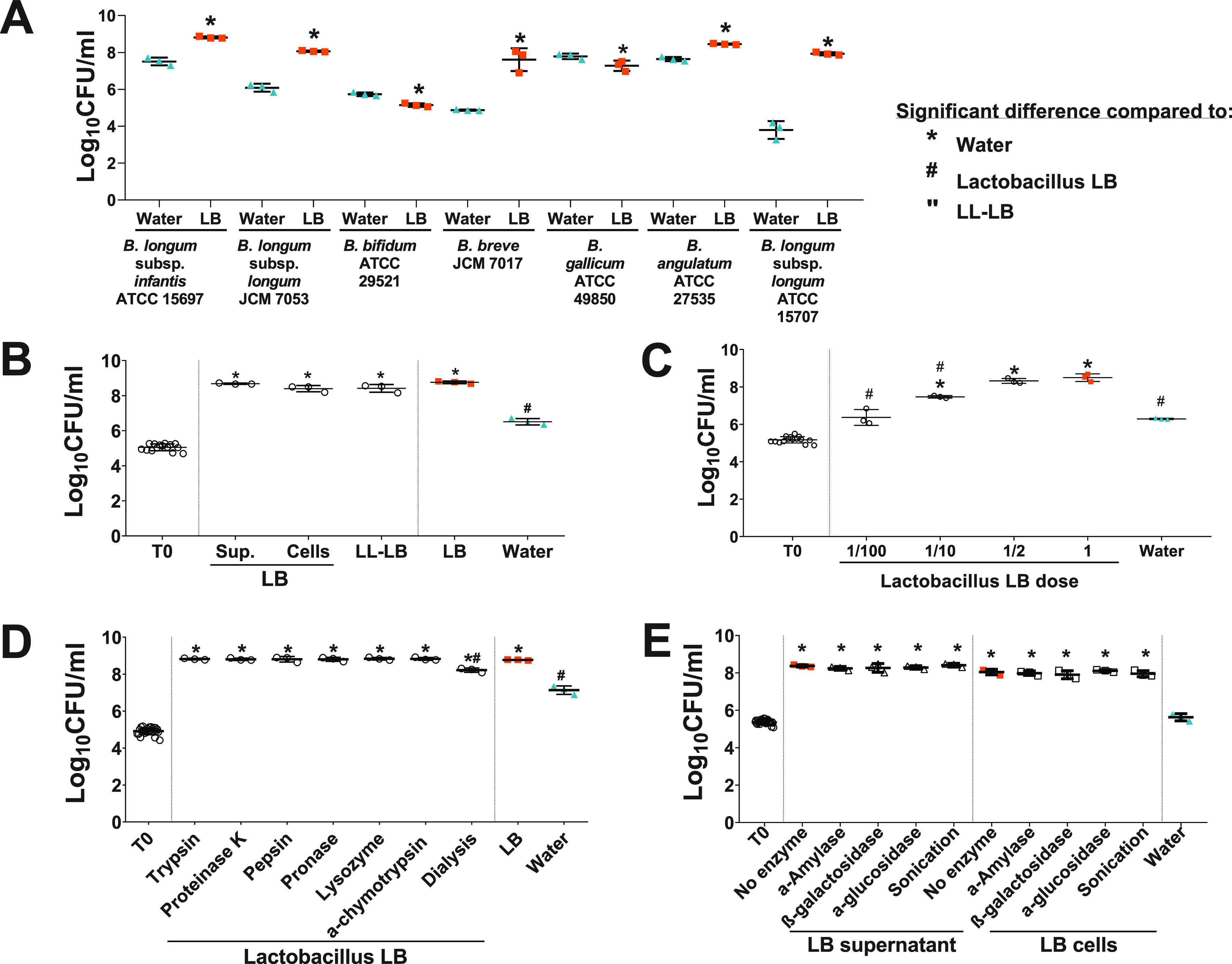
Twenty-four hours of growth of bifidobacterial in pure culture in 10× diluted media. (A) Effect of Lactobacillus LB (LB) on the growth of a range of infant- and adult-associated Bifidobacterium strains. Lactobacillus LB stimulated growth of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis ATCC 15697 (B1; t4 = 18.555, P < 0.0005), Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum JCM 7053 (t4 = 15.626, P = 0.003), Bifidobacterium breve JCM 7017 (t4 = 7.667, P = 0.016), Bifidobacterium angulatum ATCC 27535 (APC 329; t4 = 12.065, P < 0.0005), and Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum ATCC 15707 (APC 2744; t4 = 14.603, P < 0.0005). The growth of only two strains, Bifidobacterium bifidum LMG 11041 (ATCC 29521; t4 = −7.432, P = 0.002) and Bifidobacterium gallicum ATCC 49850 (APC 838; t4 = −2.828, P = 0.047), was not stimulated. (B) Effect of Lactobacillus LB components, i.e., supernatant, cells, and low-lactose Lactobacillus LB (LL-LB) on B. longum subsp. infantis ATCC 15697 growth. (C) Effect of Lactobacillus LB dose on B. longum subsp. infantis ATCC 15697 growth. (D and E) Effect of enzymatically or physically treated Lactobacillus LB on B. longum subsp. infantis ATCC 15697 growth. *, significant change compared to water supplementation. #, significant change compared to Lactobacillus LB. “, significant change compared to LL-LB supplementation.
