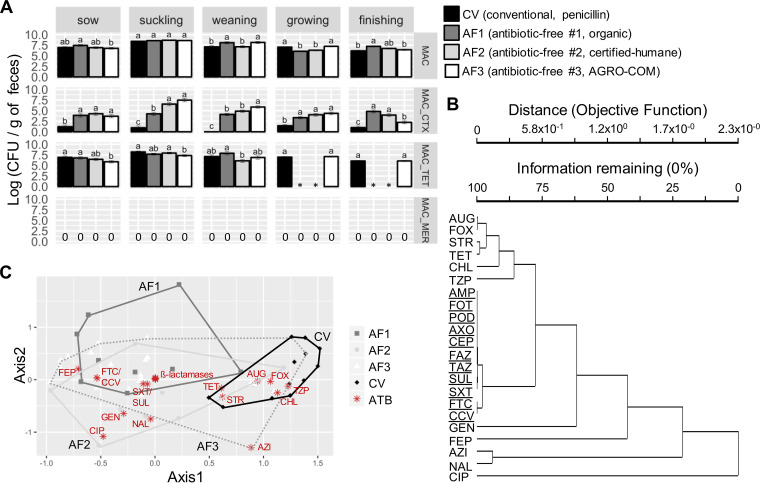
FIG 1.
Antibiotic-resistant Enterobacteriaceae according to animal type and husbandry. (A) The bars represent the least-square means plus or minus standard error of mean for log transformations of CFU per gram of feces on MacConkey agar plates (MAC) without supplementation or supplemented with cefotaxime (_CTX), tetracycline (_TET), or meropenem (_MER). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used to compare the least-square means from the same animal type reared in the different husbandries. Different letters on top of bars indicate significantly different results (P < 0.01). Missing data are indicated by asterisks, while zeroes mark the absence of colonies. (B) Hierarchical cluster analysis based on Bray-Curtis distances of the AST profiles with group average as the linkage method between the antibiotics tested on 247 bacterial strains isolated from feces. Antibiotics of the β-lactam/sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim cluster are underlined. (C) Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMS) plot of the AST profiles of 247 isolates from feces of animals reared in all four husbandries. Stars represent antibiotics as indicated, while geometric shapes represent the grouping of individual isolates. The antibiotics tested are as follows: ampicillin (AMP), amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (Augmentin; AUG), piperacillin-tazobactam (TZP), cefazolin (FAZ), cephalothin (CEP), cefotaxime (CTX), cefpodoxime (POD), ceftazidime (TAZ), ceftriaxone (CRO), cefotaxime-clavulanic acid (FTC), ceftazidime-clavulanic acid (CCV), cefepime (FEP), cefoxitin (FOX), imipenem (IMP), meropenem (MER), sulfisoxazole (SUL), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT), tetracycline (TET), gentamicin (GEN), streptomycin (STR), azithromycin (AZI), ciprofloxacin (CIP), nalidixic acid (NAL), and chloramphenicol (CHL).