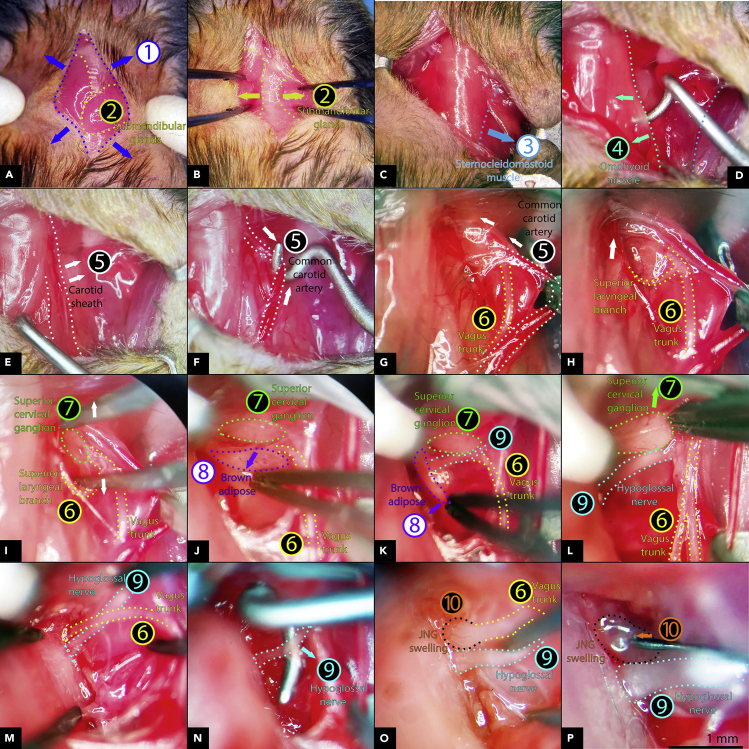
Figure 3.
Intraganglionic CCK-SAP delivery to JNG
(A) Midline incision ① to expose the submandibular glands ②.
(B) Expose of the trachea by retracting the submandibular glands ② sideways.
(C–E) Retract the sternocleidomastoid muscle laterally ③(C) and the omohyoid muscle medially ④ (D) to expose the carotid sheath ⑤(E).
(F) Penetrate the carotid sheath with blunt a spinal cord hook and separate the common carotid artery (⑤ dotted lines) from the carotid.
(G and H) Slide the spinal hook along the common carotid artery toward the skull base and tear the rostral carotid sheath and connective tissue to uncover the vagus trunk and superior laryngeal branch ⑥.
(I–K) Carefully shred down the brown adipose tissue ⑧ to gain access to the superior cervical ganglion ⑦ and the root of the hypoglossal nerve ⑨.
(L and M) Push the superior cervical ganglion ⑦ rostrally to expose the hypoglossal nerve roots ⑨ and the vagus nerve ⑥.
(N) Separate and pull the hypoglossal nerve ⑨ caudally away from the vagus nerve root with a spinal cord hook.
(O) Clean view of the JNG swelling ⑩ rostral to the hypoglossal nerve ⑨ and immediately adjacent to the cranium.
(P) Insert NanoFil needle tip medially into JNG ⑩, Scale bar, 1 mm.