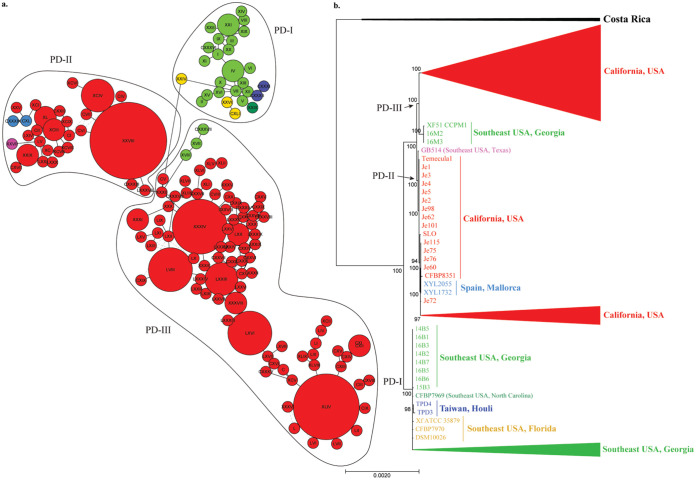
FIG 1.
Maximum likelihood (ML) tree and haplotype network showing phylogenetic and geographic diversification of worldwide PD-causing subsp. fastidiosa isolates. Color represents isolates from the same geographical location: California (red), Texas (pink), Georgia (green), North Carolina (dark green), Florida (yellow), Spain (light blue), and Taiwan (dark blue). PD-causing strains have been divided into three phylogenetically supported clades (PD-I, PD-II, and PD-III). (a) Haplotype network of PD-causing subsp. fastidiosa isolates. Haplotypes belonging to each PD-causing clade are shown within black circles. Roman numbers identify detected haplotypes (I-CXLI). The size of the circle indicates the number of isolates belonging to each haplotype. (b) ML tree of PD-causing subsp. fastidiosa isolates. The tree was built using the core genome alignment without removing recombinant segments. Bootstrap values mark branch support. Arrows point toward the base of PD-causing clades (-I to -III).