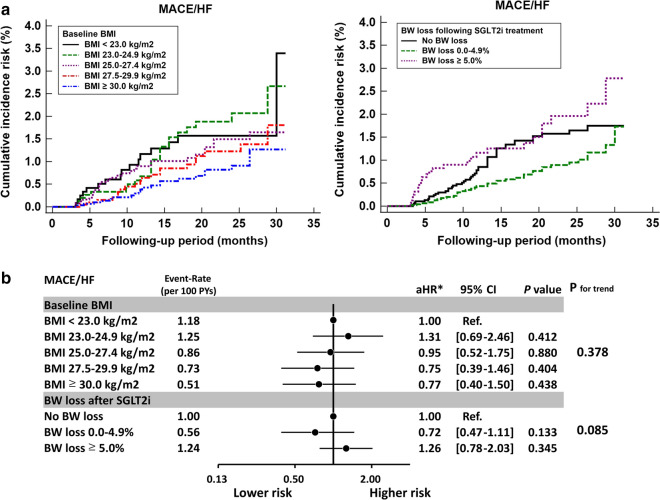
Fig. 6.
Major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) or heart failure (HF) hospitalization risk in patients with T2DM in different categories of baseline BMI and BW loss following SGLT2i treatment. Cumulative incidence risk of MACE/HF for T2DM patients in different categories of baseline BMI and BW loss following SGLT2i treatment. a Neither baseline BMI nor posttreatment BW loss predicted the risk of MACE/HF hospitalization after multivariate adjustment (P for trend > 0.05). b *Risk of outcome was adjusted for age, sex, different SGLT2i drugs and dosage, baseline comorbidities as shown in Tables 1, 2, HbA1c, eGFR, and use of antiplatelet therapy, statin, angiotensin system inhibitor, and all anti-hypoglycemic agents. HF: heart failure; MACE: major adverse cardiovascular event AF: atrial fibrillation; CI: confidence interval; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c: glycated hemoglobin A1c; aHR: adjusted hazard ratio; SGLT2i: sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor; T2DM: type 2 diabetes mellitus; BMI: body mass index; BW: body weight; SE: standard error; MRA: mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; TZD: thiazolidinedione